What are the test performance requirements for paint in building elasticity?
Architectural elastic medium coating is mainly used in wall coating, and it is applied between the primer and the top coat to cover the small cracks caused by the expansion and contraction of the base material and give a specific decorative effect to decorate and protect the building. role. It is suitable for elastic intermediate coatings made of synthetic resin emulsion, various pigments, extender pigments and additives as the main raw materials in a certain proportion. Today we will introduce the regulations of HG/T 4567-2013 on the detection of paint in building elastic materials. Before testing, we need to understand the classification of paint in building elasticity. According to different performance requirements, we divide architectural elastic medium paint into two types: type I and type II.
Testing requirements
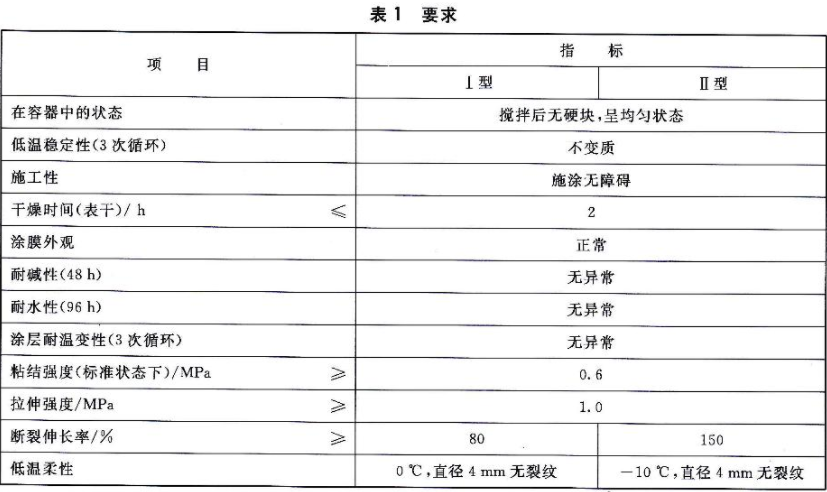
1. State in the container: First, we open the container and stir with a spatula or stirring rod, and allow precipitation at the bottom of the container. If Type Ⅰ and Type Ⅱ are easy to mix evenly after stirring, it is rated as "uniform without hard lumps after stirring".
2. Low-temperature stability: Place the type I and type II samples in a low temperature environment for 3 consecutive cycles. If neither the type I nor type II samples deteriorate, it is considered up to the standard.
3. Constructability: If there is no difficulty in the construction process of type I and type II samples, it will be rated as "no barriers to application".
4. Drying time: If the surface-drying time of type I and type II samples is less than or equal to 2 hours, it is regarded as up to standard.
5. Appearance of coating film: The test requires visual observation of type I and type II samples under scattered sunlight. If the coating film is uniform and there is no coating film pathology such as sagging, blooming, pinholes, cracking and peeling, it is rated as "normal".
6. Alkali resistance: We immerse the type I and type II samples in the specified solution for 48 hours, and visually observe after taking them out. If two of the three test pieces do not show any pathological phenomena of coating film such as blistering, cracking, and peeling, It was rated as "no abnormality".
7. Water resistance: In addition to sealing the edge, the back of the type I and type II samples needs to be sealed before testing. Soak the three test panels in the specified solution for 96 hours, if two of the three test panels do not show any abnormalities in the coating film such as blistering, cracking, peeling, powder falling, and obvious discoloration, it can be rated as "no abnormality".
8. Coating resistance to temperature denaturation: we need to conduct 3 cycle tests. First, immerse the type I and type II samples in water at (23±2)°C for 18 hours, then freeze them in an environment of (-20±2)°C for 3 hours, and finally put them into (50±2)°C for heat drying. The time is 3h. If two of the three test panels do not show any abnormalities in the coating film such as pulverization, bubbling, cracking, peeling, and obvious discoloration, it can be rated as "no abnormality".
9. Bonding strength: If the bonding strength of Type I and Type II samples under standard conditions is ≥0.6MPa, it is considered qualified.
10. Tensile strength: If the tensile strength of both type I and type II samples under standard conditions is ≥1.0MPa, it is considered qualified.
11. Elongation at break: If the test result is that the elongation at break of the type I sample is ≥80%, and the elongation at break of the type II sample is ≥150%, it is considered qualified.
12. Low-temperature flexibility: If the test result shows that the type I sample has no cracks in the diameter of 4mm at 0°C, and the type II sample has no cracks in the diameter of 4mm in the environment of -10°C, it is considered qualified.
- 1Tensile machine application in various industries
- 2Technical analysis of key parameters of Tensile machine: Scientific selection from force measurement accuracy to Power system
- 3Tensile machine purchasing guide [dry version]
- 4Application and structure principle of low/high Temperature Test Chamber
- 5Talking about the performance test of epoxy resin film coated on PET
- 6Principle, application and selection of low/high Temperature Test Chamber for plastic belt
- 7Principle, application and selection of fire-proof coatings low/high Temperature Test Chamber
- 8Principle, application and selection of ultra low/high Temperature Test Chamber
- 9Principle and application of desktop low/high Temperature Test Chamber
-
-
-
CHINA NBC-1024-2 Tensile Tester 5T$ 6635.00
-
-
-







