What are the standard requirements for different detection properties of silicone drying insulating paints?
Silicone, that is, organosilicon compounds. Because it has both the properties of organic materials and inorganic materials, it is widely used in chemical industry, construction, transportation, and other fields. Insulating varnish, that is, insulating coating, is divided into varnish and colored varnish. As a special paint in the paint category, it transmits the action and influence of electricity by induction rather than conduction.
Today we will introduce the regulations of HG/T 3375-2003 on silicone drying insulating varnish. It is suitable for silicone drying insulating varnish formulated from polymethylphenylsiloxane and xylene. It is Class H insulating material. Before testing, we need to understand the classification of silicone drying insulating paint. We divide it into type I and type II according to its use.
Type I is mainly used for impregnating electrical coils that operate at 250°C~300°C for a short period of time and electrical coils for motors that operate at 180°C~200°C for a long time.
Type II is mainly used for impregnated glass wire and glass cloth, and can also be used as a protective layer for semiconductor tubes.
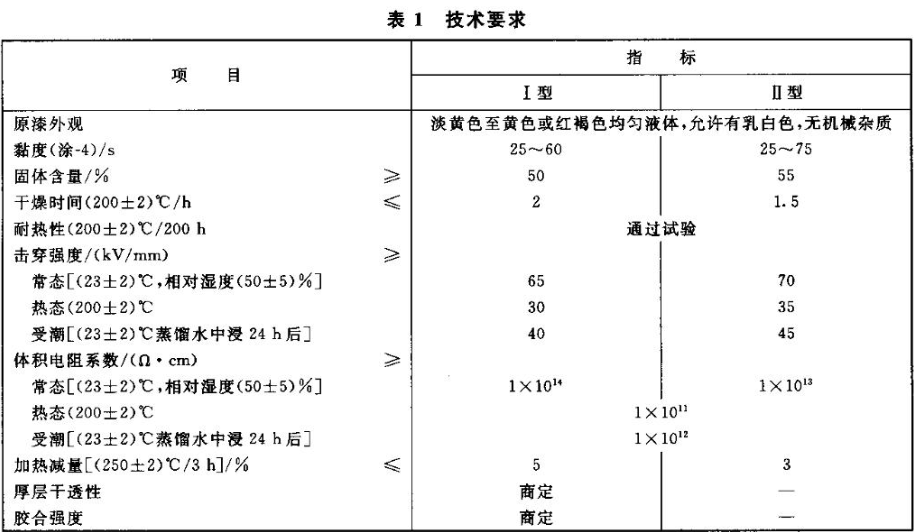
Item detection
1. Appearance of original paint: Use visual inspection method, if the observation result of type Ⅰ and type Ⅱ is light yellow to yellow or reddish brown uniform liquid, milky white is allowed, and there is no mechanical impurity, it is considered to meet the standard.
2. Viscosity: Use Tu-4 cup to test, if the outflow time of type I is within 25s-60s, and the outflow time of type II is within 25s-75s, it is considered to be up to standard.
3. Solid content: The baking temperature during the test is based on the temperature of the silicone paint. If the solid content of type I is ≥50% and the solid content of type II is ≥55% after baking, it is regarded as up to the standard.
4. Drying time: The ambient temperature required for testing is within 200°C ± 2°C, if Type I ≤ 1h, Type II ≤ 1.5h, it is considered up to the standard.
5. Heat resistance: If the type Ⅰ and type Ⅱ can stand at 200°C±2°C for 200 hours without wrinkled skin, bubbling and other changes, it is considered to be up to the standard.
6. Breakdown strength
a. Under normal conditions, the temperature is 23°C±2°C and the relative humidity is 50°C±5°C. Type Ⅰ ≥ 65kv/mm, type Ⅱ ≥ 70kv/mm, it is considered up to standard.
b. In a hot environment, that is, the temperature is 200°C±2°C. Type Ⅰ ≥ 30kv/mm, type Ⅱ ≥ 35kv/mm, it is considered up to standard.
c. In a damp environment, that is, at a temperature of 23°C±2°C, soak in distilled water for 24 hours, take it out and dry it and observe it. If type I≥40kv/mm and typeⅡ≥45kv/mm, it is considered up to standard.
7. Volume resistivity
a. Under normal conditions, the temperature is 23°C±2°C and the relative humidity is 50°C±5°C. If type Ⅰ≥1*10^14Ω·cm, type Ⅱ≥1*10^13Ω·cm, it is regarded as up to standard.
b. In a hot environment, that is, the temperature is 200°C±2°C. If both type Ⅰ and type Ⅱ are ≥1*10^13Ω·cm, it is regarded as reaching the standard.
c. In a damp environment, that is, at a temperature of 23°C±2°C, immerse in distilled water for 24 hours, take it out and dry it and observe it. If both Type I and Type II are ≥1*10^12Ω·cm, it is considered up to the standard.
7. Heating loss: keep at 250°C±2°C for 3 hours, after taking out, if the mass value of type I is ≤5%, and the mass value of type II is ≤3%, it is regarded as up to standard.
8. Thick-layer dryness: The standard of type I thick-layer dryness is determined by the testing parties according to the actual needs of the product.
9. Adhesive strength: The dryness standard of type I thick layer is determined by the testing parties according to the actual needs of the product.
- 1Liquid viscosity measurement and application
- 2Measuring method of coating viscosity
- 3Basic Principle and Application Analysis of Paints drying time Tester
- 4Waterborne architectural coatings detection method
- 5Summary of drying time determination method for paint film and putty film
- 6Several Determination Methods of Coating drying time
- 7Viscosity: Microscopic forces inside liquids shape macroscopic properties
- 8Coating performance testing: ensuring the efficiency and mass of the painting process
- 9Film drying method: natural drying, heating drying, irradiation curing and gas phase curing
-
-
-
-
-
JINGKELIAN QNF Backtack Tester 3 pcs$ 190.00
-






