What subjects are generally tested for architectural paint color paste?
With the development of the paint industry, architectural paint colorants are valued by many professionals in the industry because of their specialization, functionality, generalization and diversification, and are mainly used in the field of architectural interior and exterior wall coatings. It is suitable for water-based colorants (except transparent colorants) prepared from various organic pigments, inorganic pigments, wetting and dispersing agents and various additives.
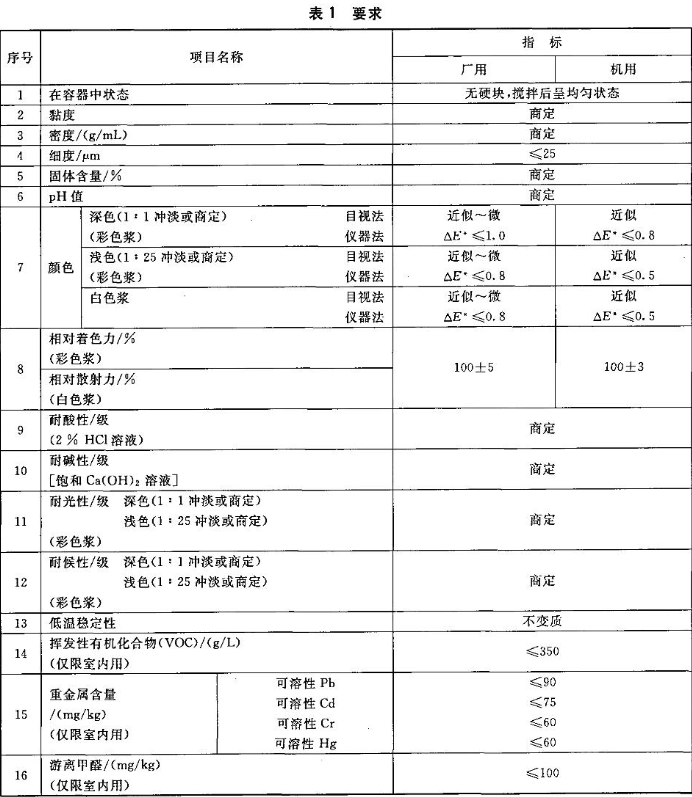
Today we will introduce the testing requirements for architectural paint colorants stipulated in the HG/T 3951-2007 standard. Before testing, we need to divide architectural paint colorants into two categories according to the way the colorants are used, namely factory use and machine use.
Item detection
1. State in the container: If the factory sample and the machine sample have no hard lumps after stirring and are in a uniform state, it is considered to be up to the standard.
2. Viscosity and density: The testing parties determine the viscosity and density standards of factory samples and machine samples according to the actual needs of the product.
3. Fineness: If during the testing process, the fineness of both factory samples and machine samples is ≤25μm, it is regarded as up to standard.
4. Solid content and PH value: The testing parties determine the solid content and PH value standards of factory samples and machine samples according to the actual needs of the product.
5. Color
a. Use the visual method to observe the 1:1 diluted dark color paste, and then use the instrument method to observe the color paste. If the factory sample is approximately ~ micro △ E ≤ 1.0, and the machine sample is approximately ~ micro △ E ≤ 0.8, it is considered to be up to standard.
b. Use the visual method to observe the 1:25 diluted light color paste, and then use the instrument method to observe the color paste. If the factory sample is approximately ~ micro △ E ≤ 0.8, and the machine sample is approximately ~ micro △ E ≤ 0.5, it is considered to be up to standard.
c. Use measuring method or instrument method to observe the white pulp. If the factory sample is approximately ~ micro △ E ≤ 0.8, and the machine sample is approximately ~ micro △ E ≤ 0.5, it is considered to be up to standard.
6. Relative tinting strength: The color paste is used for testing. If the relative tinting strength of the factory sample is within the range of 100±5, and the relative tinting strength of the machine sample is within the range of 100±3, it is considered to be up to standard.
7. Relative scattering power: use white paste to test, if the relative tinting power of the factory sample is within the range of 100±5, and the relative tinting power of the machine sample is within the range of 100±3, it is regarded as up to standard.
8. Acid resistance: Immerse the factory samples and machine samples in 2% HCI solution, and the acid resistance standards of the factory samples and machine samples are determined by the testing parties according to the actual needs of the products.
9. Alkali resistance: Immerse the factory samples and machine samples in saturated Ca(OH)2 solution, and the acid resistance standards of the factory samples and machine samples are determined by the testing parties according to the actual needs of the products.
10. Light fastness: use 1:1 diluted dark color paste and 1:25 light color paste for testing, and the testing parties determine the light fastness standards of factory samples and machine samples according to the actual needs of the product.
11. Weather resistance: 1:1 diluted dark color paste and 1:25 light color paste are used for testing, and the testing parties determine the weather resistance standards of factory samples and machine samples according to the actual needs of the product.
13. Low-temperature stability: Place the factory samples and machine samples in a low-temperature environment. If the test result shows no deterioration, it is considered to be up to standard.
14. Volatile organic compounds: In the indoor environment, if the volatile organic compound content of the factory samples and machine samples is ≤350g/L, it is considered to be up to the standard.
15. Heavy metal content: If the soluble Pb≤90mg/kg, Cd≤75mg/kg, soluble Cr≤60mg/kg, and soluble Hg≤60mg/kg of the factory sample and machine sample, it is regarded as up to standard.
16. Free formaldehyde: After testing, if the free formaldehyde content of the factory sample and the machine sample is ≤100mg/kg, it is considered to be up to the standard.
- 1Liquid viscosity measurement and application
- 2Coating fineness test method and influencing factors
- 3Measuring method of coating viscosity
- 4MB35 halogen Moisture Analyzer: a tool for accurately measuring volatile matter
- 5Viscosity: Microscopic forces inside liquids shape macroscopic properties
- 6Detection Steps of Coating Fineness and Operation Method of Ground Gauge
- 7Coating fineness measurement and its role in Coating quality control
- 8Density conversion concentration formula
- 9Thermostatic bath working principle and its application in viscosity measurement







