What is the measurement principle of surface tension?
Surface tension is defined as the excess force per unit length on a surface; if its direction of action is to cissing the surface, the tendency of the system considered positive to reduce the surface area is the result of excess surface energy because surface atoms are subject to a different environment compared to atoms in the body. The surface tension of liquid and polymer melts can be measured by methods such as capillary, Dunoy rings, William plate 27, 38, and pendant. We will focus on two methods: capillary height method and pendant method.
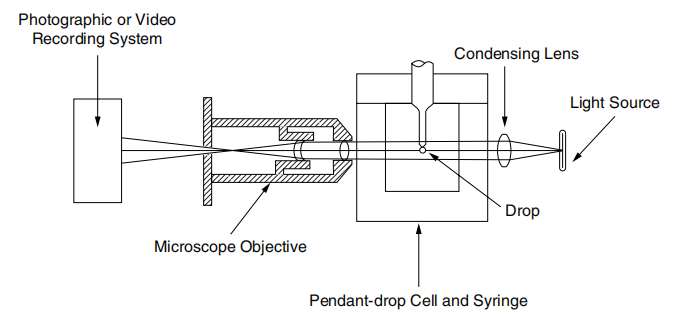
图 2.2 悬垂法的实验装置
The capillary height method is best suited for low viscosity liquids as it takes a long time for the system to reach equilibrate for high viscosity liquids. It has been reported that up to 4 days of polyester ethylene melts that need to reach equilibrate at 200 ° c Figure 2.1 illustrates the capillary height method. In the equilibrated state, the force exerted around the meniscus due to surface tension must be equilibrated with the weight of the liquid column. Ignoring the weight of the liquid above the meniscus, the following approximate equation can be obtained:
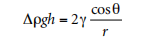
Where Δp is the difference in Density between the liquid and air, g is the gravitational constant, h is the height of the column, γ is the surface tension, θ is the contact angle, and r is the radius of the capillary. In practice, it is difficult to accurately measure the vertical contact angle and the known and uniform radius. To more accurately determine the surface tension, there are various ways to calculate the weight of the liquid above the meniscus.
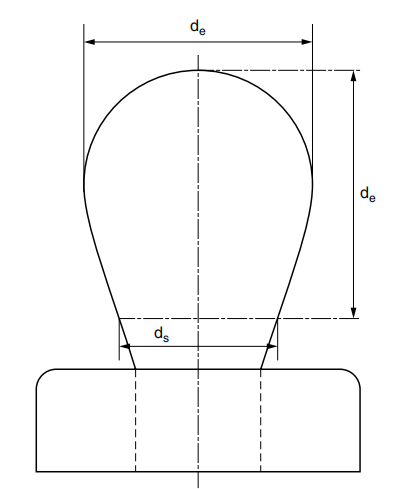
图 2.3 典型的悬垂曲线
The hanging drop method is a very general technique for the measurement of surface tension of liquids as well as the interfacial tension between two liquids. Andreas et al. Use this method for the measurement of surface tension of various organic liquids. Wu and Roe have widely used this method for the measurement of surface and interfacial tension in many polymer liquids and melts.
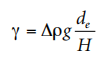
The experimental setup shown in Figure 2.2 includes a light source, a droplet battery and a syringe assembly in a constant temperature room, as well as a microscopic camera setup. Figure 2.3 shows a typical pendant shape. The surface tension of the liquid is given by the following formula, where de is the maximum (equatorial) diameter of the dangling droplet and H is the Correction factor depending on the shape of the droplet; H is related to the measurable shape correlation factor S, which is defined as where ds is The diameter of the dangling droplet in the selected plant at a distance from the droplet vertex de (see Figure 2.3). There are tables showing the value of 1/H as a function of S.
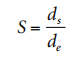
Recently, many significant improvements have been made in data collection and profiling of overhanging droplets. Photographic recording and measurement of 15-17 overhanging droplets have been replaced by direct digitalization of video images. The ability to measure the entire droplet profile has led to the development of new algorithms for droplet profile analysis.
- 1Water surface tension measurement based on Electronic Balance
- 2Working principle of mechanical liquid meter interfacial tensIon Meter
- 3Comparison of Liquid Surface/Interfacial Tension Testing Methods: Plate vs. Ring Method
- 4Selection guide for Surface Tensiometers
- 5Application principle and precautions of platinum ring Surface Tensiometer
- 6Coating surface tension and its effects
- 7Coating process surface tension factor
- 8Three commonly used detection methods for surface tension
- 9Ceramic ink-jet surface tension, viscosity and solutions










