What are the commonly used testing instruments in textile laboratories?
Textile Tensile Testing Machine
When textiles are subjected to external mechanical forces such as stretching, compression, bending, and friction, damage such as fracture, tearing, and bursting will inevitably occur. But you can determine the duration of the textile based on these damages. So what to do? Textile Tensile Testing Machines are experts in testing the duration of textiles driven by external forces according to the degree of tearing and breaking. Can also be used on leather, plastic, paper and more.
First of all, the two ends of the material sample are generally clamped on two fixtures respectively, and a certain distance is kept. The grips do not stop separating and stretching the material sample at a constant velocity until the sample is broken. You can then record the change in stress and measure the peak force and yield strength of the product. This kind of Tensile Testing Machine was roughly divided into two categories: hydraulic Tensile Testing Machine and electronic Tensile Testing Machine in the early days. However, the current market share of hydraulic Tensile Testing Machines is very small due to poor accuracy, failure to meet the required standards, and lack of ability to test equipment with higher force values.
During the test, the textile Tensile Testing Machine needs to be connected to a computer for collecting and analyzing data, and making test results and reports accordingly.
Martindale Abrasion and Pilling Tester
This instrument is specially designed for testing the abrasion and pilling of various textiles. First, the circular sample is placed on the grinding head and brought into contact with the standard woolen abrasive fixed on the grinding machine under the specified pressure. The instrument will automatically stop if the circular specimen has been rubbed the specified number of times. We need to compare the standard parameters with the number of textiles that show abrasion and pilling after the experiment to obtain relevant data. The Martindale Abrasion Pilling Tester is used to test the abrasion resistance and pilling properties of cotton, linen, silk woven fabrics, and other textiles. In addition, it can also be used to detect membrane materials, knitted fabrics, wool, artificial leather, synthetic leather, gloves, labor protection products, etc.
The instrument can perform two tests:
1) Fabric pilling
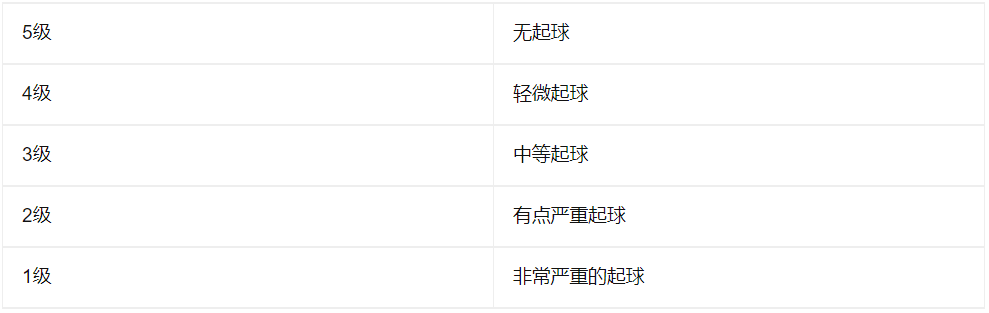
Test This test is applicable to both knitted and woven fabrics. During this process, the textile sample and the rubbing cloth are rubbed against each other on the grinding platform, so that some geometric shapes are formed. After that, we need to compare the damaged sample with the standard sample. According to the different degrees of pilling, the samples can be divided into five grades.
2) Abrasion resistance test of textiles
The fabric sample needs to be fixed on the grinding platform and rubbed with a friction cloth attached to the grinding head. Under the guidance of atomic absorption spectrometry, we can obtain the abrasion resistance of textiles from the damage degree and mass loss of the sample and the change of appearance.
The machine can generally be customized with 4, 6, and 9 stations to meet various needs of customers. It also allows each site to be tested simultaneously for increased testing efficiency.
Moisture Management Tester
Moisture Management Testers, also known as Rapid Moisture Management Testers, measure dynamic liquid transfer properties, water absorption and perspiration properties as they flow through fabrics or other materials, helping textile manufacturers understand the handling capabilities of their fabric materials and predict textiles The ability to wick sweat in actual use.
Moisture meters assess absorption performance by measuring changes in electrical conductivity. First, we need to place the sample horizontally between the upper and lower sensors with concentric pins, and place a drop of the prepared solution on the center of the upper surface of the sample. Next, we need to measure and record the change in resistance as the solution flows across the sample. The resistance data is used to calculate the moisture content. Once the results are obtained, the fabric will be graded according to the water absorption by comparing with predetermined indicators.
The moisture management Tester can test the dynamic liquid transport performance of knitted and woven fabrics, non-woven fabrics and other textiles, and is mainly used to test the following three properties of the product.
1) Moisture absorption rate
The time it takes for the inner and outer surfaces of the fabric to absorb moisture.
2) Dispersion/drying rate
The rate at which liquid moisture diffuses across the inner and outer surfaces of the fabric.
3) One-way transfer capability
Liquid moisture transfers unidirectionally from the inner surface of the fabric to the outer surface. In addition, the moisture management Tester is simple and convenient to operate, and can quickly, stably and accurately test the moisture content of the sample. The instrument is equipped with a transparent protective cover, which can effectively prevent liquid from spilling during the test.
Sweat protection stove
As we all know, whether the clothing is qualified or not depends mainly on the comfort of the wearer. We feel uncomfortable if body heat and moisture cannot flow freely due to the material of the fabric. Fortunately, we can test the heat and moisture resistance of various textiles by using the Sweating Guarded Hotplate to simulate the skin environment. According to the test results, we can test the comfort of the textile. It consists of a human skin simulation test board, an automatic water supply system, a wind speed stabilization system, and a test host. It is also equipped with an environmental chamber where temperature and humidity can be closely controlled to ensure that there is specific and required hardware for testing.
Test Principle
A fixed aluminum or copper plate is heated in a standard test atmosphere until a certain constant temperature is reached. Then you can test the heating power. In the same way, after spreading the test cloth on the test board, we can test the heating power of the test cloth under the same conditions. The thermal resistance or moisture resistance value of the test sample can be determined according to the differential power between the test board and the test board area. The greater the heat and moisture resistance value of clothing, the stronger the ability to hinder the flow of body heat and moisture, which also means the more uncomfortable.
Hydrostatic Head Tester
Hydrostatic pressure Tester, also known as hydrostatic pressure Tester, is mainly used to measure the water penetration resistance of fabrics under hydrostatic pressure.
At standard atmospheric pressure, the fabric is subjected to rising water pressure until water droplets appear on the back of the fabric. At the same time, the water pressure value you measure is what we call hydrostatic pressure. The more hydrostatic pressure a fabric can withstand, the better it will be water-resistant or impermeable. For different fabric materials, there are different test methods. The hydrostatic head Tester can be used to test many fabrics and films, including canvas, coated cloth, drape, rainwear, and geotextiles. It is often used for waterproof testing of outdoor sportswear, waterproof fabric testing, liquid permeability testing and blood permeability testing of protective materials such as medical protective clothing.
Test Principle
Fix the sample in the specified test area. You then need to use an Air Compressor to put 0-5 bar air into a tank with distilled water and apply the water to the specimen under pressure. Testing can be performed based on dynamic or static methods.
(1) Dynamic method: When the sample is not in contact with water, the pressure rises at a constant speed, and specified water droplets are attached to the sample, the pressure test is carried out.
(2) Static method: test the water permeability of the sample under a certain pressure for a certain period of time.
Air permeability Tester
As we saw with our Testers, breathability played a key role in creating a comfortable fabric. Some industrial fabrics such as aircraft parachutes and filter cloths have higher requirements for sportswear and windproof and coldproof clothing. Air permeability Testers are widely used to test the resistance of fabrics to the passage of air (airflow), such as woven, knitted and non-woven textile materials, and medical masks. The principle of the air permeability test is to calculate the amount of air flowing through the fabric per unit time when the air passes through the fabric vertically under a certain pressure, and generate a pressure difference between the front and back of the fabric.
The air permeability Tester can be used to test various fabrics, such as woven fabrics, non-woven fabrics, airbag fabrics, blankets, fleece fabrics, knitted fabrics, multi-layer fabrics and cotton linter fabrics. It can also test airflow over viscous thick, elastic porous objects, such as polyurethane foam.
Testing Procedure: You will need to take the following steps.
1) First cut the prepared standard sample to the required size.
2) Carefully select the fixing ring of the test piece and install it on the Tester.
3) Press the button of the nozzle.
4) Turn on the power of the instrument and set the parameters before starting the machine.
5) Put on the start button to operate the Tester.
6) The Tester compresses the sample and begins to test the air permeability. When the set pressure difference is reached, the Tester will automatically release the sample, calculate the data and stop running.
7) Continue to test another sample and perform data processing until there are enough effective test times (the current number will be displayed on the screen). You can print test results or view them on the air permeability and differential pressure displays.
Multifunctional Flammability Tester
At present, the testing and research of the flame resistance of textiles has become a widely concerned issue at home and abroad. The flame resistance of textiles is not only related to the types of fibers, dyes and various finishing agents, but also related to its structure, shape, burning environmental conditions, and atmospheric temperature and humidity. The multifunctional combustion Tester is used to test the flammability of various textile materials. For example: vertically oriented flame spread performance testing of large tents such as garments, curtains, fabrics, awnings, textile door covers, and burning time of textiles covered with pile (such as fluffy, pile, tufted or similar surfaces).
Test Principle
Install the completed sample or material sample on the corresponding fixture of this Tester, burn it with a specified flame for a certain period of time, and measure relevant data (such as burning time, burning rate), so that you can evaluate its burning performance.
There are many ways to test combustion performance. However, a generally accepted measurement method for testing combustion performance has not yet been proposed. In addition, all methods are used to semiquantitatively test the relative combustion of the specimens.
Washing Fastness Tester
The color fastness of textiles is a routine textile testing item. According to different requirements and simulation scenarios, the color fastness test can generally be divided into conventional washing color fastness test, perspiration fastness test, wet and dry Mo test, light fastness test, chlorine bleach fastness, saliva fastness, etc.
The color fastness to washing refers to the fading degree of the dyed fabric after soaping in a specific environment, which can be tested according to the original fading and staining of the white cloth. The original fading is related to the degree of fading of the dyed fabric before and after soaping; white cloth dyeing refers to sewing white cloth and dyed cloth together in a certain way, and then dyeing the white cloth through the fading of the dyed cloth after soaping. The degree of fading or staining should be tested under the specified light source and measured on a standard gray card scale. The test results can be divided into 5 grades. A rating of 5 is recommended and a rating of 1 is worst. At present, the domestic and foreign test method standards of the project are relatively complete,
Test Principle
Configure the test piece according to the standard (if it is a white cloth stain test, you need to sew the test piece with white cloth) → then configure the soap that meets the standard and method → then wash the specific standard method with water → wash and dry → use a gray sample card or instrument score.
laboratory conditioning room
Laboratory conditioning chambers are also called environmental chambers or climate chambers, used as environmental simulation systems and equipment for laboratories and factories. Its function is to adjust the temperature and humidity, and to conduct high-low temperature alternating tests on various materials before testing. The temperature, humidity and time of the test can be programmed by the laboratory conditioning room. Additionally, during testing, environmental chambers can regulate the custom temperature and humidity required by many testing instruments, including textile testing instruments, helping to obtain more accurate test results relative to the testing instrument. Now, let's figure out how the conditioning room works.
1) Good simulation. Within a certain tolerance range, the external environment of product use, storage and transportation can be simulated.
2) Trial and error. The same product can be tested multiple times through one environmental Test Chamber or different environmental Test Chambers. By repeating this process, we can obtain more comparable test results even when we put the same product in the same laboratory environment.
3) Under good control. When using this cabinet, you can freely adjust the environmental parameters. That is, you can protect your product from damage by limiting the environmental parameters within certain tolerances, eliminating uncontrolled environmental conditions to ensure the accuracy of your simulations.
4) Wide range of applications. Specifically, the constant temperature and Humidity Chamber can be used for quality inspection of daily production and life, electronics, electrical, communications, instrumentation, vehicles, plastic products, metals, food, chemicals, building materials, medical care, aerospace, sanitary ware, etc. .
5) Extraordinary safety performance. The environmental chamber has the characteristics of safe and reliable operation and long service life. Various protection devices, alarm systems, and safety interlocks are also equipped with environmental testing equipment.
In short, the laboratory environmental chamber can accurately simulate the complex natural environment of high temperature, extreme temperature and humidity, low temperature and high humidity. Therefore, it can test the cold resistance, heat resistance, dryness and humidity resistance of the product to make it more durable.
Infrared laboratory dyeing machine
Infrared experimental dyeing machine, also known as infrared sample dyeing machine, is a general-purpose laboratory dyeing equipment, which can be used to test high-temperature samples such as knitted fabrics, woven fabrics, yarns, cotton, loose fibers, zippers, and shoe nets.
It is specially designed for dyeing industry, chemical industry, raw material, cloth industry, high temperature dyeing and proofing machine. In addition, we can accurately simulate real production conditions and test the dyeability of materials to achieve the desired process effect. In addition, the machine heats the material through infrared rays without other media, so the temperature can be controlled more accurately.
The main advantages are as follows.
1) Quick response
2) Save operating costs
3) Effective heating
4) Uniform heat transfer
5) Ability to measure the actual temperature in the dyeing cup
6) Easy to clean, smoke-free and pollution-free work space