Fabrics with UV radiation protection factor
Our skin is increasingly exposed to the sun's UV radiation mainly due to our lifestyle and the trends set by the fashion industry. However, there has also been an increase in the textile sector's awareness of protection against such radiation.
While it is true that there are tissue-intrinsic parameters that affect more or less radiation protection, this is not a factor that influences and can be controlled. The textile industry is researching the effectiveness of protection when applying certain dyes or depositing particles on fabrics, but it is also immersed in the development of fibers that can absorb UV radiation.
UPF (Ultraviolet Protection Factor)
Just as the protection factor can be determined in sunscreen, it can be quantified in textiles. In fact, there are several standards that allow the classification of fabrics according to UPF, such as UNE-EN 13758 or AS/NZ 43399.
Each of them classifies the degree of protection on a different scale, although both are based on UPF obtained through the standard UNE we refer to. So, while UNE-EN 13758 only allows the labeling of garments with a UPF greater than 40 - indicating that said garments offer excellent protection - the AS/NZ 4339 standard establishes categories related to different UPF values. In each case, it needs to be included in the tag.
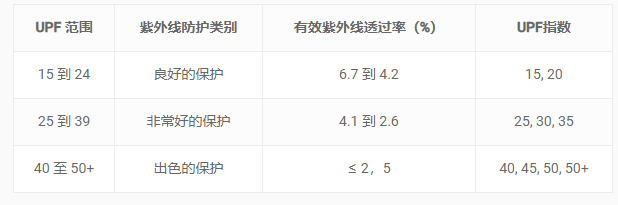
Labeling and classification of fabrics according to UV radiation protection factor (Standard AS/NZ 4339:1996)
UPF calculation
After measuring according to the method stipulated in the standard, the formula widely used to calculate UPF is as follows:
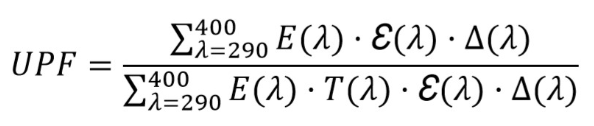
E (λ): solar irradiance
ε (λ): Spectrum of erythema action according to CIE
T(λ): Spectral transmittance of the fabric
Δ (λ): the measured wavelength range, in nm.
λ: wavelength, in nanometers.
Factors to Consider When Calculating UPF
As we have seen, the spectrum of solar irradiance is applied as a correction factor when calculating UPF, which includes issues such as latitude, altitude, ozone layer, time of year or time of day, since UV radiation reaching the Earth's surface does not Always arrives at the same scale. In this way, real UV radiation conditions are simulated in the laboratory based on measurements made in a specific geographical area.
Another factor considered in the UPF calculation is the erythema action spectrum, a correction that takes into account the effects of different types of UV radiation on humans.
The calculation of UPF also takes into account the transmittance coefficient of the fabric, i.e. the ultraviolet radiation that is neither absorbed nor reflected by the fabric, but passes through it. A Spectrophotometer is used to perform this type of measurement.
ultraviolet radiation
Ultraviolet radiation is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength between approximately 400nm and 15nm, so it ranges from wavelengths shorter than the violet end of the visible spectrum. Therefore, it is a wavelength invisible to the human eye.
This type of radiation can change the behavior of molecules, and prolonged exposure to UV radiation is known to increase the risk of serious skin damage and disease.

- 1The working principle and application of rubber UV aging Test Chamber
- 2Application of UV aging Test Chamber in mobile phone shell
- 3UV aging Test Chamber for sealant aging test
- 4Application of UV aging Test Chamber in silica gel test
- 5UV UV aging Test Chamber for weathering test of exterior-wall latex paint coatings
- 6How does UV aging Test Chamber test the ageing resistance of exterior paints?
- 7Correct calibration method and process for UV aging Test Chamber
- 8Is it possible to measure the hidden percentage of artificial heather, fences and hedges?
- 9Measurement of the protection factor of sunscreen