Tester for film-forming process, physical drying, chemical curing, and minimum film-forming temperature of coatings
The purpose of producing and using paint is to obtain the desired paint. The film forming process directly affects the application effect of the coating and the various properties of the coating. The film-forming process of the coating includes two processes: coating the surface of the object to be coated and forming a solid and continuous paint film. The thin liquid film formed after applying the liquid paint on the surface of the object to be coated is called a wet film; the wet film forms a solid continuous paint film in different ways according to different mechanisms, which is called a dry film. The process in which the paint forms a dry film from a wet film is the process of drying and curing the paint to form a film.
Due to the different film-forming resins, the film-forming mechanisms of various coatings are also different. A correct understanding of the film-forming mechanism of coatings can further understand the performance of coatings and help people use coatings correctly.
There are two main methods of coating film formation: physical drying and chemical curing. Chemical curing can be divided into oxygen polymerization curing, curing agent curing, steam curing and so on.
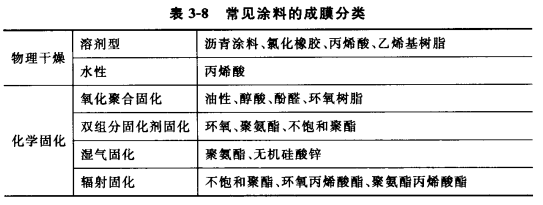
1. Physical drying
There are two forms of physical drying: solvent volatilization and polycondensation of polymer particles to form a film. For solvent-based coatings, after coating, the solvent evaporates into the atmosphere, completing the drying process of the coating film. Commonly used coating products are asphalt coatings, vinyl coatings, chlorinated rubber coatings and acrylic coatings. The commonality of these coatings is as follows.
(1) Reversibility. Over months or even years, the film can dissolve on its own or with stronger solvents. Solvent molecules penetrate the binder molecules, forcing them to separate and breaking down the binder.
(2) Solvent sensitivity, due to reversibility, these coatings are not resistant to their own solvents or stronger solvents.
(3) Film formation does not depend on temperature, because there is no chemical reaction in the film formation process.
(4) Thermoplastic, physically drying coatings soften at elevated temperatures.
Dispersion paints, such as latex paints, change from particle aggregation to molecular aggregation by contacting and extruding polymer particles during the evaporation of water to form a continuous paint film. The commonality of these coatings is as follows.
a. Reversibility At a certain temperature, the paint film can be redissolved by itself or stronger binders or solvents; however, it is not possible to redisperse the paint film by adding water alone.
b. Sensitivity to solvents. Compared with the above points, similar or stronger solvents will have a certain impact on the paint film.
c. The formation of paint film is related to temperature. At the softening point, the binder particles can fuse together, usually at a temperature of 5°C or higher. For the construction temperature, it should be controlled above 10°C.
d. Like solvent-based coatings, it is thermoplastic.
e. Good recoating performance.

2. Chemical curing
Chemically cured coatings are composed of converted film-forming materials, mainly formed through chemical reactions. The film-forming material polymerizes into a polymer film during construction.
Coatings with natural oil as film-forming material, as well as natural resin coatings containing oil components and alkyd resin coatings, phenolic resin coatings and epoxy ester resin coatings synthesized from petroleum, all rely on oxidative polymerization to form films. This is a free radical chain polymerization. The molecular weight of unsaturated fatty acids in these coatings increases by oxidation, and the rate of oxidative polymerization is related to the number and position of methylene groups and the rate of oxygen transfer. To speed up the oxidative drying process, a dryer can be used. In most cases, the oxygen head first attacks the Cc bond, or the α-methylene group. The use of metal salt desiccants, such as cobalt, manganese, lead, etc., will facilitate the attack of oxygen. Because multivalent metal salts can act as oxygen carriers, or combine with double bonds to form new compounds that are more susceptible to oxygen attack.
Coatings that require a curing agent to react to form a film are usually divided into two components. One component is the base material, which contains resins, solvents, pigments and fillers, and the other component is the curing agent. When in use, pour the curing agent into the substrate and stir evenly before use. Common epoxy coatings, polyurethane coatings and unsaturated polyester coatings.
The curing mechanism of coatings involves several other chemical reactions or polymerization processes.
(1) The molecules of the moisture-curing substrate react with water vapor, such as inorganic zinc silicate coatings and one-component polyurethane coatings.
(2) The carbon dioxide molecules of the cured substrate react with carbon dioxide in the air, such as inorganic zinc-rich coatings of sodium silicate/potassium silicate.
(3) The silicone curing reaction triggered by high temperature needs several hours at 200°C to reach the degree of curing.
Chemical curing coatings have the following basic properties.
a. Irreversibility, the cured paint film is insoluble.
b. Solvent resistance is a result of irreversibility.
c. Film formation rate depends on temperature. For example, some coatings have specific requirements for minimum film-forming temperatures. Below this temperature, the film will not cure.
d. It is non-thermoplastic. The molecules of the binder do not move in a highly cross-linked state, and do not change even at high temperatures. For example, paint films do not soften at high temperatures.
e. Strict retest intervals. Recoating between coats will be required until curing is fully complete. Coated surfaces that have been fully cured will require roughening prior to application of a coat of paint.

- 1Minimum film forming temperature (MFFT): from theory to practice
- 2What is the minimum film forming temperature?
- 3What are the properties of dry film?
- 4GB/T 20623 Emulsion Performance Testing Scheme for Architectural Coatings [Instrument List]
- 5How to choose a good latex paint?
- 6How to understand the minimum film forming temperature of emulsion?
- 7What is the minimum film formation temperature? How to reduce MFT
- 8Jingke QMB-II Minimum Film Formation Temperature Tester Instruction Manual
- 9What are the mass control indicators of Architectural coatings?





