General Impact Test for Paints and Coatings - ASTM D2794
Since coatings such as paints, varnishes, conversion coatings, and related coated products are subject to impact damage during their manufacture and service life, this impact resistance test method has been found useful in predicting the impact resistance of coatings. ASTM D 2794 provides a procedure for rapidly deforming coating films and their substrates by impact and evaluating the effects of such deformation.
The organic coating to be tested is applied to four or more suitable thin metal panels. After the coating is cured, the standard weight is dropped for a certain distance, and the indenter is struck to deform the coating and the substrate. Indentation can be intrusion or extrusion. By gradually increasing the distance the weight is dropped, usually 1 inch (25 mm) at a time, the point at which failure typically occurs can be determined.
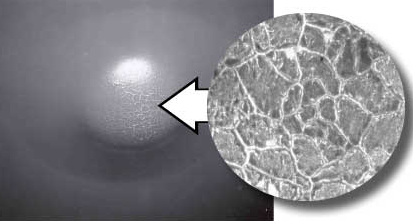
Films often fail by cracking (see photo below), which can be made more apparent by using a magnifying glass, applying a copper sulfate (CuSO4) solution to the steel, using a pinhole Detector, or by pulling tape testing to determine the amount of coating removed.
Once visible cracks are identified, repeat the test five times at that level, and five times above and below that level. Of course, these confirmatory tests are performed in random order, so consecutive tests are not performed at the same height or on the same panel.
Reference: ASTM D2794 Standard Test Method for Resistance of Organic Coatings to the Effects of Rapid Deformation (Impact)
Relevant ASTM standards include:
ASTM D1186 – Test Method for Nondestructive Measurement of Dry Film Thickness of Nonmagnetic Coatings Applied to Ferrous Substrates;
ASTM D609 – Practice for the preparation of cold-rolled steel panels for testing paints, varnishes, conversion coatings, and related coating products;
ASTM D823 – Practice for producing films of paints, varnishes, and related products of uniform thickness on test panels.
- 1Application of Pendulum Impact Instrument in Encasement Aluminum Plastic Paper Composite
- 2How to Evaluate Mechanical Properties of Cigarette Pack Aluminized Paper with Pendulum Impact Meter
- 3Application of Pendulum Impact Instrument in Nylon Membrane
- 4Sheet for Pendulum Impact Meter Application
- 5What are the specific applications of pendulum Impact Meter in Plastic film?
- 6Pendulum impact test How to test transport packages?
- 7Bevel impact test for transport packages
- 8Determination of impact resistance of paint film - impact Tester
- 9Effect of Epoxy Emulsion Types on Properties of Paint Film
陈深填 - 《华南理工大学 化学与化工学院 》





