LEEB160C accuracy high color screen integrated printing Leeb Hardness Tester standard D probe
SELeeb leeb160C Leeb Hardness TesterSPEC
Leeb leeb160C Leeb Hardness TesterDetails
Leeb leeb160C Leeb Hardness TesterPacking list
- SKU
- NB043834
- Error of indication/Repeatability
- ±6HLD(HLD=760)/ 6HLD(HLD=760)
- Measurement range
- 100-990(HLD)
- Identifiable Impact Device
- D、G、C、DL、DC、D+15、DS
- Impact device socket
- LEMO socket
- Measurement direction
- 360°
- Hardness system
- HL、HB、HRC、HRB、HV、HS
- Power
- Lithium battery rechargeable battery
- Charging Specifications
- 9v/1800mA
- Storage function
- 600 groups
- shell material
- Plastic shell
- Dimensions
- 230×86×46mm
- Weight
- 400g
- optional
- Special-shaped support ring, Impact device, standard test block, communication software, printing paper
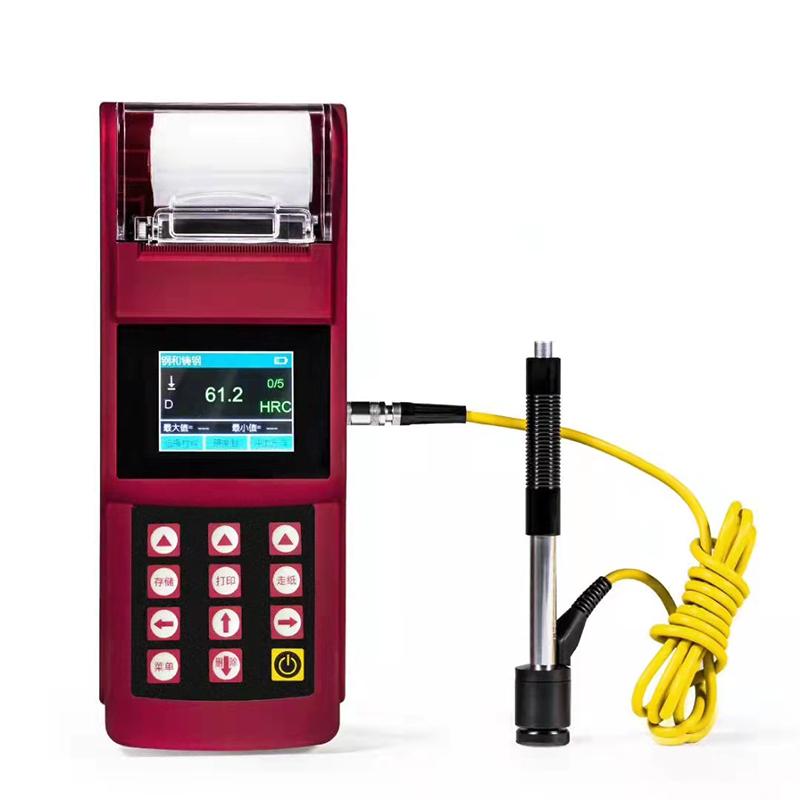

Overview
leeb160C is a hardness measuring instrument that can be integrated with built-in printer, tolerance setting and other functions, with a built-in thermal printer, which supports on-site instant printing to ensure the fairness of measurement results and data storage and traceability. Using full Chinese display, menu-based operation, simple and convenient operation. This machine can directly display the hardness values of Richter, Brinell, Rockwell, Vickers, Shore and so on. The instrument is small, portable, and highly stable, suitable for harsh operating environments, and resistant to vibration, shock, and electromagnetic interference.

Features
D-type precision impact device is adopted;
Industrial shell design, sturdy, small, portable, high stability, suitable for harsh operating environments, resistant to vibration, shock and electromagnetic interference;
The integrated design of the host and printer is convenient for users to print the test results on site;
Large-screen color screen display, rich in information, intuitive, easy to operate and read;
The upper limit and lower value and overrun alarm can be set in advance;
It has the function of power on value indication software calibration to ensure that the data is used under different specifications and standards in any industry;
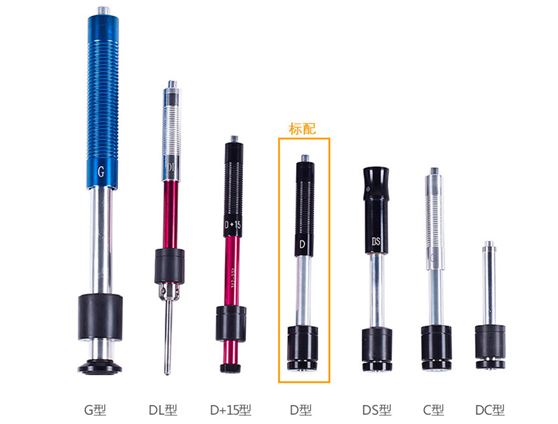
It can be equipped with 7 different impact devices, which do not need to be calibrated when replacing and are automatically recognized;
It can store 600 sets of measured values, full menu, backlight display, easy to operate;
It can be equipped with software, with rich functions such as transmission of measurement results, measurement value storage management, measurement statistical analysis, printing measurement report, etc., which is suitable for higher requirements of quality assurance activities and management;
Built-in large-capacity lithium-ion rechargeable battery and charge control circuit;
Continuous work for no less than 200 hours (when printing is not on), automatic sleep, automatic shutdown and other power-saving functions.
Applicable Materials
Steel & Cast Steel, Alloy Tool Steel, Stainless Steel, Grey Cast Iron, Ductile Iron, Cast Aluminium Alloy, Copper-Zinc Alloy (Brass), Copper-Tin Alloy (Bronze), Pure Copper, Forged Steel.
Applications
1. It is suitable for on-site hardness testing of heavy workpieces, mold cavities, workpieces with very narrow experimental space, bearings and other parts, large parts and non-detachable parts
2. Failure analysis of pressure vessels, turbine-generator sets and their equipment, as well as material differentiation of metal material warehouses
3. The hardness testing of products in the process of mass production can meet the testing requirements with a set of general standards
4. For hardness testing of annealing, tempering, quenching and other heat treatments, it is necessary to pay attention to the thickness of the hardened layer when selecting the model, and if the hardened layer is too thin, it is necessary to choose a C-type impact device
5. When testing the hardness of the bearing, it is necessary to pay attention to the bearing diameter, if the diameter is too small, the special-shaped support ring needs to be selected
6. When the gear hardness is tested, if the gear is too small, the DL impact device needs to be selected
7. When inspecting castings, if it is difficult to perform the finish, it is necessary to choose the G-type impact device.
Test Scope
| material | Hardness | Impact device | ||||
| D/DC | D+15 | C | G | DL | ||
| Steel and cast steel | HRC | 17.9~68.5 | 19.3~67.9 | 20.0~69.5 | 20.6~68.2 | |
| Steel and cast steel | HRB | 59.6~99.6 | 47.7~99.9 | 37.0~99.9 | ||
| HRA | 59.1~85.8 | |||||
| HB | 127~651 | 80~638 | 80~683 | 90~646 | 81~646 | |
| HV | 83~976 | 80~937 | 80~996 | 80~950 | ||
| HS | 32.2~99.5 | 33.3~99.3 | 31.8~102.1 | 30.6~96.8 | ||
| Steel forged steel | HB | 142~651 | ||||
| CWT、ST | HRC | 20.4~67.1 | 19.8~68.2 | 20.7~68.2 | ||
| Alloy tool steel | HV | 80~898 | 80~935 | 100~941 | ||
| Stainless steel | HRB | 46.5~101.7 | ||||
| stainless steel | HB | 85~655 | ||||
| HV | 85~802 | |||||
| GC. IRON | HRC | |||||
| Gray iron | HB | 93~334 | 92~326 | |||
| HV | ||||||
| NC、IRON | HRC | |||||
| nodular cast iron | HB | 131~387 | 127~364 | |||
| HV | ||||||
| C.ALUM | HB | 19~164 | 23~210 | 32~168 | ||
| Cast aluminium alloy | HRB | 23.8~84.6 | 22.7~85.0 | 23.8~85.5 | ||
| BRASS | HB | 40~173 | ||||
| Copper-zinc alloy | HRB | 13.5~95.3 | ||||
| BRONZE copper-tin (aluminum) alloy | HB | 60~290 | ||||
| COPPER pure copper | HB | 45~315 | ||||
Note: When using the Leeb Hardness Tester to measure, the measured workpiece needs to be suitable for the corresponding test conditions, mainly three requirements: the weight of the workpiece is not less than 2KG, the small thickness is not less than 10mm, the surface roughness is not more than 1.6um, and it needs to be firmly supported or densely coupled when it is not suitable for the above conditions!
Indication error and repeatability
| serial number | Type of impact device | Standard Leeb block hardness values | Indication error | Repeatability of the indication |
| 1 | D | 760±30HLD | ±6 HLD | 6 HLD |
| 530±40HLD | ±10 HLD | 10 HLD | ||
| 2 | DC | 760±30HLDC | ±6 HLDC | 6 HLD |
| 530±40HLDC | ±10 HLDC | 10 HLD | ||
| 3 | DL | 878±30HLDL | ±12 HLDL | 12 HLDL |
| 736±40HLDL | ||||
| 4 | D+15 | 766±30HLD+15 | ±12 HLD+15 | 12 HLD+15 |
| 544±40HLD+15 | ||||
| 5 | G | 590±40HLG | ±12 HLG | 12 HLG |
| 500±40HLG | ||||
| 6 | C | 822±30HLC | ±12 HLC | 12 HLC |
| 590±40HLC |

The Leeb Hardness Tester meets the standard
1. GB/T 17394.1-2014 "Hardness test on metallic materials – Part 1: Test methods"
2. GB/T 17394.2-2012 "Hardness test on metal materials – Part 2: Inspection and calibration of Hardness Tester"
3. GB/T 17394.3-2012 "Hardness test on metal materials – Part 4: Calibration of standard hardness blocks"
4. GB/T 17394.4-2014 "Hardness test on metallic materials – Part 4: Standard value conversion table"
5. The design is based on the standard: "Technical Conditions for Leeb Hardness Tester" JB/T 9378-2001
Requirements for the surface of the test specimen
The condition of the specimen surface should meet the relevant requirements in the test scope table.
The surface temperature of the sample should not be too high and should be less than 120°C.
The surface roughness of the specimen should not be too large, otherwise it will cause measurement errors. The surface of the specimen is exposed to metallic luster, and is flat, smooth, and free of oil.
Specimen weight requirements: for heavy specimens greater than 5kg, no support is required, and specimens weighing 2-5kg, specimens with overhangs and thin-walled specimens should be supported by objects during testing to avoid deformation, deformation and movement of specimens caused by impact. For medium-sized specimens, place them on a flat, firm plane, and the specimen is placed smoothly without shaking.
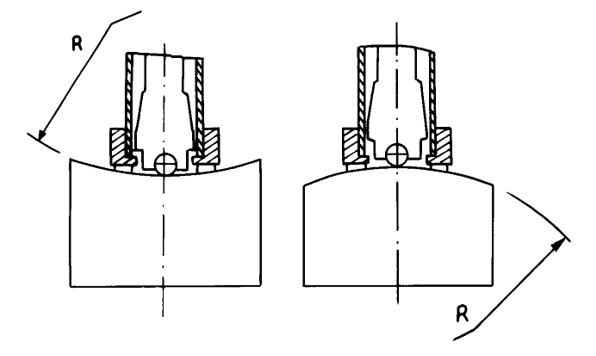
Curved sample: The test surface of the specimen is flat. When the radius of curvature R of the measured surface is less than 30mm (D, DC, C, DL type impact device) and less than 50mm (G type impact device), small support rings or special-shaped support rings should be used for testing.
The specimen should have the corresponding thickness, and the small thickness of the specimen should conform to the provisions of the impact device table.
For specimens with a case-hardened layer, the depth of the hardened layer should be in accordance with the table of impact devices.
coupling
1) For light specimens, it needs to be tightly coupled with a strong supporting body, the two coupling surfaces need to be flat and smooth, the amount of couplant should not be too much, and the test direction should be perpendicular to the coupling plane;
2) When the specimen is a large-area plate, long rod or bent piece, even if the weight and thickness are large, it may still cause deformation and instability of the specimen, resulting in inaccurate test values, so it should be firmly fixed or supported on the back of the test point.
The specimen itself should be less than 30 gauss.
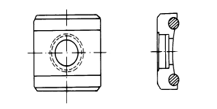
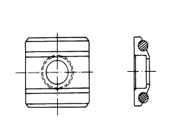
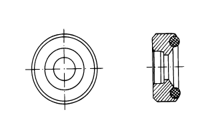
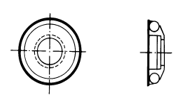
Heterosexual support ring (optional)
| Model | Schematic diagram of special-shaped support rings | remark |
Z10-15 |
| Measuring the outer cylindrical surface R10~R15 |
| Z14.5-30 | Measuring the cylindrical surface R14.5~R30 | |
| Z25-50 | Measuring the outer cylindrical surface R25~R50 | |
HZ11-13 |
| Measuring the inner cylindrical surface R11~R13 |
| HZ12.5-17 | The cylindrical surface of the inner test is R12.5~R17 | |
| HZ16.5-30 | The cylindrical surface of the test is R16.5~R30 | |
K10-15 |
| Measuring spherical SR10~SR15 |
| K14.5-30 | Measuring spherical SR14.5~SR30 | |
HK11-13 |
| Measuring the spherical SR11~SR13 |
| HK12.5-17 | Measuring the spherical SR12.5~SR17 | |
| HK16.5-30 | Measuring the inner spherical SR16.5~SR30 | |
UN |
| cylindrical surface outside the test, |
| The radius is adjustable R10~∞ |
Impact device (optional)
| Impact device | DC/D/DL/DS | D+15 | C | G |
| Impact energy | 11mj | 11mj | 2.7mj | 90mj |
| Impact body mass | 5.5/5.5/7.2/5.5 g | 7.8 g | 3.0 g | 20 g |
| Ball joint hardness | 1600 HV | 1600 HV | 1600 HV | 1600 HV |
| Ball head diameter | 3 mm | 3 mm | 3 mm | 5 mm |
| Ball head material | Tungsten carbide | Tungsten carbide | Tungsten carbide | Tungsten carbide |
| Diameter of the impact device | 20/20/6/20 mm | 20 mm | 20 mm | 30 mm |
| Length of impact device | 86/147/202/138 mm | 162 mm | 141 mm | 254 mm |
| Impact device weight | 50/75/60/70 g | 80 g | 75 g | 250 g |
| The upper hardness of the specimen | 940/940/950/940 HV | 940 HV | 1000 HV | 650 HB |
| The average surface degree of the specimen is Ra | 1.6 µm | 1.6 µm | 0.4 µm | 6.3 µm |
| Application of impact device | DC type measuring bore or cylindrical cylinder; | The D+15 type has a small, elongated contact surface and is suitable for measuring grooved or recessed surfaces. | Type C has small impact force, little damage to the measured surface, does not destroy the hardened layer, and is suitable for measuring small and thin parts and surface hardened layers. | The G type measures large and heavy castings and forgings with rough surfaces. |
| DL type measures slender narrow grooves or holes; | ||||
| Type D is used for routine measurements; | ||||
| DS type measurement line on-line detection (loading and release are completed at one time) |
- 1DL/T 1845-2018《Test method for Leeb hardness of high-alloy steels in power equipment》
- 2GB/T 13313-2008《Methods of shore and leeb hardness testing for rolls》
- 3GB/T 17394.1-2014《Metallic materials―Leeb hardness test―Part 1: Test method》
- 4GB/T 17394.4-2014《Metallic materials―Leeb hardness test―Part 4:Tables of hardness values conversation》
- 5GB/T 17394.3-2022《Metallic materials—Leeb hardness test—Part 3: Calibration of reference test blocks》
- 6GB/T 17394.2-2022《Metallic materials—Leeb hardness test—Part 2: Verification and calibration of hardness testers》
- 7GB/T 17394-1998《Metallic materials--Leeb hardness test》
- 8GB/T 17394.3-2012《Metallic materials - Leeb hardness test - Part 3: Calibration of reference blocks》
- 9GB/T 17394.2-2012《Metallic materials - Leeb hardness test - Part 2: Verification and calibration of hardness testers》
- 10JB/T 9378-2001《Leeb hardness testers》
 leeb160C
leeb160C