
MODERNER PN-II Plate viscometer for determination of flow characteristics of inks
Moderner PN-II Plate viscoMeterSPEC
Moderner PN-II Plate viscoMeterDetails
Moderner PN-II Plate viscoMeterPacking list
- SKU
- NB000720
- Display mode
- Miscellaneous
- Operating Environment
- Temperature 25 ℃ +/- 1 ℃; Humidity 65% +/- 5%
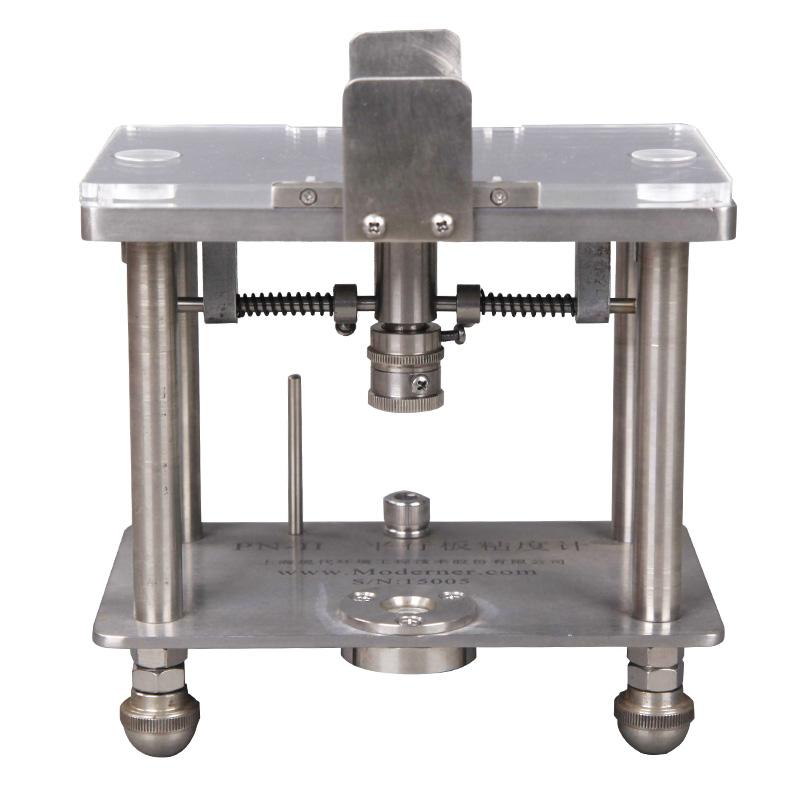

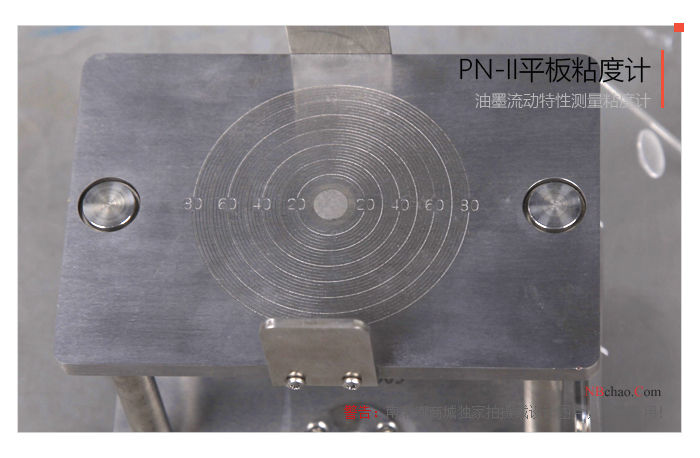
Overview of PN-II Plate Viscometer
MODERNER PN-II plate viscometer is an instrument that uses the fluidity of ink to measure the viscosity of ink. The PN-II plate viscometer has a simple and compact structure design. There are four diameters of 20, 40, 60 and 80 drawn on the surface of the plate. The round shape makes it easy to observe the spread of ink. There is an ink hole in the middle of the tablet, and parallel plates are designed on both sides.
Plate viscometer principle
Flat (parallel) plate viscometer is mainly used to measure the flow characteristics of ink. This is an instrument based on the principle of ink flow between two parallel plates.
Place a certain amount of ink (0.5 cm3) between two parallel plates placed horizontally, so that the upper plate with a certain mass (115 grams, made of transparent material) freely falls horizontally at a fixed height and presses against the ink On the machine, the ink spreads outward, and the relationship between the spreading diameter and time is measured until the maximum diameter at which the ink no longer spreads. By plotting the logarithm lg t of time t as the abscissa and the spreading diameter d as the ordinate, a characteristic curve representing the ink flow characteristics to a certain extent can be obtained. There are many circles of different diameters engraved on the surface of the lower plate so that the ink spreading can be observed and recorded. Usually read the position of the ink edge at 10 seconds, 60 seconds and 100 seconds - the number of turns, and the maximum diameter when the ink no longer spreads.
Four parameters of the ink can be measured with a parallel plate viscometer, namely apparent viscosity, yield value, slope and intercept.
1. Apparent viscosity
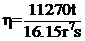
Where: ηâapparent viscosity (Pascal seconds)
t â time of measurement (seconds)
r â spread radius at time t (cm)
s â slope of the characteristic curve, equal to the difference in spreading diameter (in millimeters) at 100 seconds and 10 seconds
2. Yield value
The pressure per unit area of ââthe ink between the two plates decreases with time (because the weight of the upper plate is fixed and the ink area increases with time). When the shear stress is reduced to equal to the yield stress of the ink, the ink no longer spreads. , the spreading diameter of the ink reaches the maximum. It can be seen that there is a functional relationship between the yield stress S0 of the ink and the maximum spreading diameter dm of the ink measured with a flat plate viscometer. The value of yield stress can be obtained from the formula of rheology theory
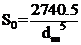
Where: S0 â Yield stress (N/mm2)
dm â Maximum ink spreading diameter (cm)
But its value is usually not calculated, but the maximum diameter dm is used to express its yield value. There is also a practice of using the spreading diameter at 30 minutes as the maximum spreading diameter.
3. Slope and intercept
Slope is a characteristic parameter representing the length of ink drawing. The greater the slope, the longer the ink filament head, and vice versa. The intercept is related to the concentration of the ink. The larger the intercept, the thinner (softer) the ink. On the contrary, the thicker (harder) the ink is.
There is a linear relationship between the ink spreading diameter d measured with a flat plate viscometer and the logarithm of time lg t. The slope and intercept of the straight line can be obtained:
s=d100-d10
I=d10-s
In the formula: sâ slope
IâIntercept (mm)
d10âInk spread diameter at 10 seconds (mm)
d100âInk spreading diameter at 100 seconds (mm)
The spreading diameter d60 at 60 seconds is called the fluidity value.
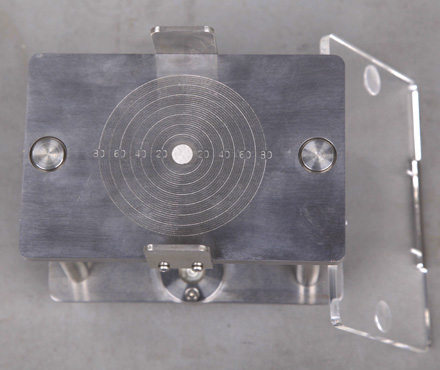
Product picture of plate viscometer
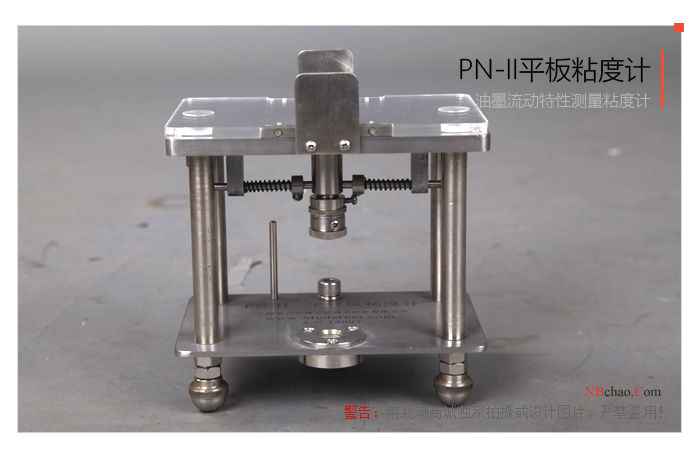
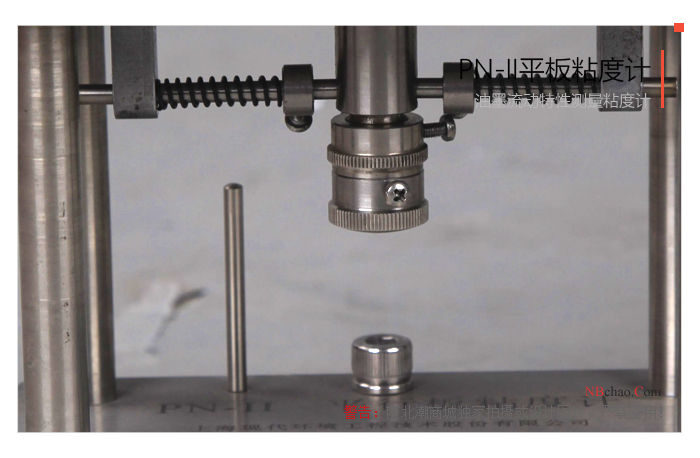
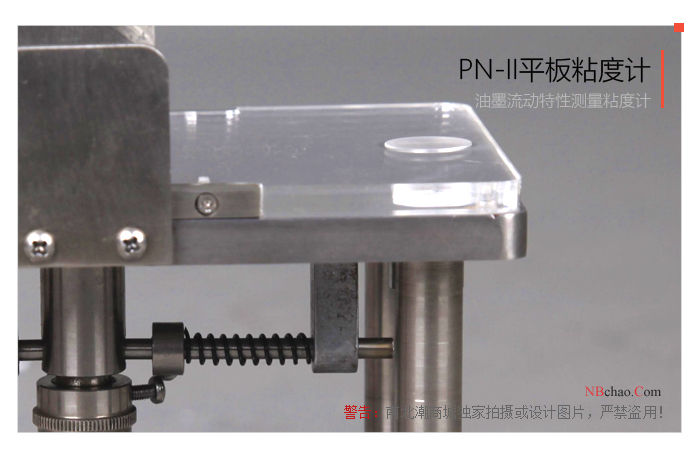



Operation and use of plate viscometer
1) Clean the ink holes and the upper and lower parallel plates (1 and 12) of the instrument and let them dry.
2) Adjust the three adjustment screws (8) and confirm the level of the instrument with the level bulb (9).
3) Rotate the guide post (2) appropriately to raise the upper parallel plate (1) and secure it, and pull down the handle (7).
4) Put the ink into the ink hole in the middle of the lower parallel plate. Make sure the ink surface is level with the surface of the lower parallel plate. Be careful not to create bubbles and gaps. When loading ink, you can remove the upper parallel plate and put it back on the guide post after installation.
5) Push the handle (7) upward and start the stopwatch at the same time. The ink is pushed to the center of the lower parallel plate, and the upper parallel plate will fall horizontally at the same time.
6) Read the spread diameter of the ink (in millimeters) at 10 seconds, 60 seconds, and 100 seconds.
7) Read the maximum spread diameter of the ink (in millimeters).
8) Calculate according to the above formula, obtain the measurement data and keep records.
9) Notes: The experiment should be carried out under constant temperature conditions, with a temperature of 25℃±1℃ and a humidity of 65%±5%.
Use and maintenance of plate viscometer
After use, clean the flat plate viscometer and put it in the box and place it securely without bumping it. The instrument should be placed upright, with the upper parallel plate (plexiglass plate) placed on the lower parallel plate to prevent deformation. The upper parallel plate should be replaced if it is not flat for a long time and the weight is insufficient (115g±2g).
If it is found that the upper end surface of the shaft and the lower parallel plate (12) are not on the same plane after the central shaft (4) bounces up, adjustment should be made. Unscrew the small column (5) and insert it into the hole at the lower end of the central shaft; loosen the set screw of the adjusting nut (6) and adjust the adjusting nut appropriately so that the upper end surface of the central shaft and the lower parallel plate are on the same plane; lock Tighten the set screw of the adjusting nut and return the small column to its original position.


 PN-II
PN-II

