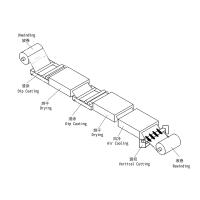
What are the requirements for preparing test samples for aqueous dip paint?
Water-based dipping paint is formulated from water-based resins, pigments, extender pigments, various additives and deionized water. It integrates the conversion, stability, agglomeration characteristics and poly-permeability of nanoparticles. Its technology is based on domestic forward. It is suitable for water-based paint applied by dip coating, and can be used for protective coating on the surface of metal facilities such as frames and chassis of various transportation vehicles, agricultural machinery, petrochemical, T. equipment, instruments and meters, and hardware components. So what are the requirements for the preparation of test samples for water-based dip coating? That's what we're going to talk about today.
Today we will introduce the regulations of HG/T 4760-2014 on water-based dip coating. Before testing, we need to understand the classification of water-based dip coatings. We can set the baking cross-linking curing type dip coatings as Type I. For example, water-based acrylic resin, water-based polyester resin, water-based alkyd resin, etc. are used for the resin; amino resin, blocked isocyanate, etc. are used for the cross-linking agent; low-temperature baking or room temperature dry dipping paint is set as Type II. For example, the resin adopts water-based acrylic emulsion, water-based alkyd resin, water-based epoxy ester resin, etc.
Item detection
1. State in the container: First, we open the container and stir with a spatula or stirring rod, and allow precipitation at the bottom of the container. If Type Ⅰ and Type Ⅱ are easy to mix evenly after stirring, it is rated as "uniform without hard lumps after stirring".
2. According to the provisions of GB/T 13452.2-2008, test the thickness of the coating film.
3. The test of curing conditions shall be tested by the relevant data provided by the paint supplier.
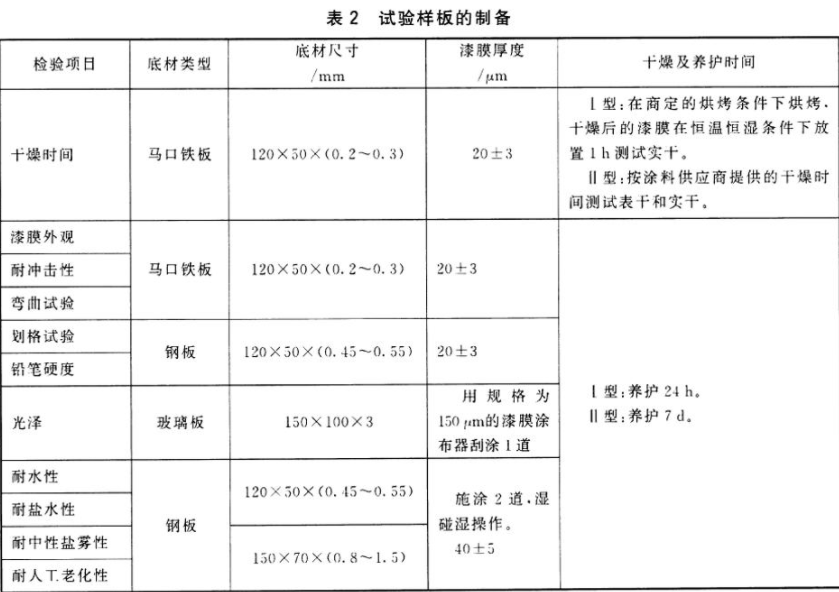
4. Sample preparation:
a. First, we take a 120 × 50 × (0.2~0.3) tin plate to test the drying time. In the test, the thickness of the spray paint needs to reach 20±3μm to ensure the accuracy of the test. We bake type Ⅰ according to the baking conditions specified by the test parties, and place the dried paint film under constant temperature and humidity conditions for 1 hour to test for hard drying; type Ⅱ test surface dry and hard dry according to the drying time provided by the paint supplier.
b. Take a 120 × 50 × (0.2~0.3) tin plate to test the appearance of the paint film, impact resistance and bending test. In the test, the thickness of the spray paint needs to reach 20±3μm to ensure the accuracy of the test. If the curing time of type I is 24h, and the curing time of type II is 7d, it is considered qualified.
c. Take a 120 × 50 × (0.45~0.55) steel plate for cross-cut test and pencil hardness test. In the test, the thickness of the spray paint needs to reach 20±3μm to ensure the accuracy of the test. If the curing time of type I is 24h, and the curing time of type II is 7d, it is considered qualified.
d. Take a 150 × 100 × 3 glass plate for gloss test. For the test, use a paint Film Applicator with a specification of 150 μm to scrape one coat on the glass plate. If the curing time of type I is 24 hours, and the curing time of type II is 7 days, it is considered qualified.
e. Take 120 × 50 × (0.45~0.55) steel plate for water resistance and salt water resistance test. During the test, use a paint Film Applicator with a specification of 150 μm to scrape two scratches of 40±5 μm on the glass plate, and perform according to the requirements of wet-on-wet operation. If the curing time of type I is 24h, and the curing time of type II is 7d, it is considered qualified.
f. Take 150 × 70 × (0.85~1.5) steel plates for neutral salt spray resistance and artificial aging resistance tests. During the test, use a paint Film Applicator with a specification of 150 μm to scrape two scratches of 40±5 μm on the glass plate, and perform according to the requirements of wet-on-wet operation. If the curing time of type I is 24h, and the curing time of type II is 7d, it is considered qualified.
- 1Working Principle and Application Analysis of Ceiling Salt Spray Tester
- 2Film hardness testing method: pendulum hardness, pencil hardness, etc
- 3ISO 15184 Pencil method to measure the hardness of paint film
- 4Analysis of hardness measurement by ASTM D3363 pencil method
- 5Salt Spray Tester in salt spray testing
- 6Hardware salt spray test method
- 7Purpose and method of durability testing of building materials
- 8Pencil Hardness Tester test procedure, application and different Hardness Pencil introduction
- 9Test Scheme for Temperature and Moisture Resistance of Packaged IC Chips