Coating drying time, gelling time and curing time
In the field of paints and coatings, curing time, drying time, and gelling time are three different but related concepts, each of which represents the chemical or physical change process of a coating at different stages, and here are their definitions and differences.
Drying time
definition
Drying time refers to the process in which the coating begins to lose solvent or moisture from the coated surface after application, so that the surface of the coating forms a dry solid. This process is usually achieved through the evaporation of volatile solvents or water.
importance
The drying time affects the application period of the paint and the application time of the subsequent coating. Faster drying times can improve application efficiency and productivity in paint production.
Assay method
The surface of the paint can be judged to be dry by observing the time point at which a dry film forms on the surface of the paint or by measuring it with a specific instrument. Methods include touch, mass change, or instrumental measurement.
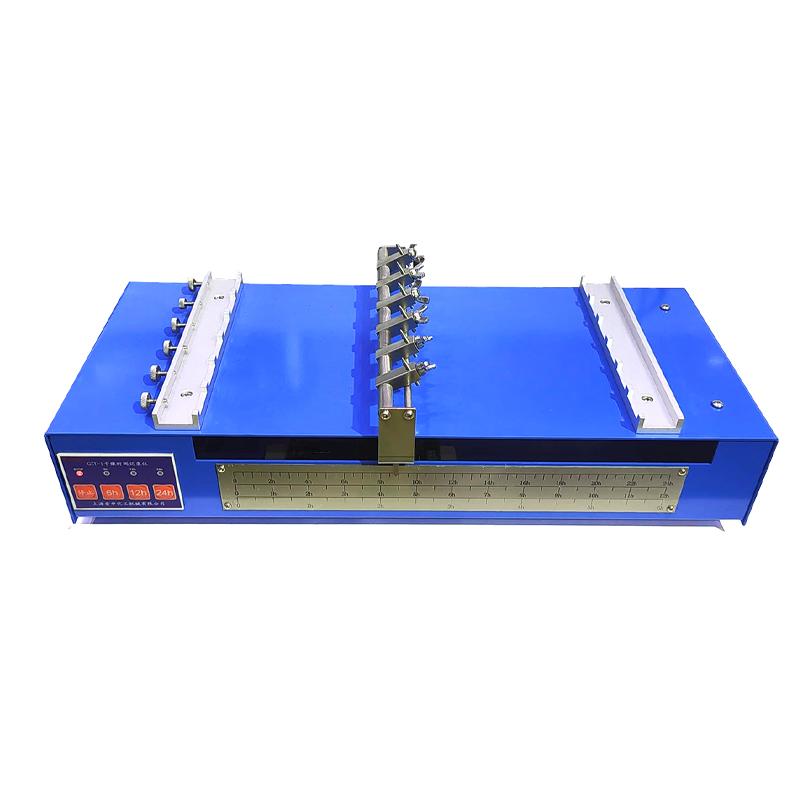

Gelling time
definition
Gelling time refers to the time it takes for a coating or resin to begin to form a gelatinous or gelling state during mixing or curing. This process is the beginning of thickening of the paint or the formation of a solid structure due to a cross-linking reaction or gelation reaction.
importance
Gelling time is often used to evaluate how quickly a coating or resin will begin to cure after mixing and how long it will work. This is very important for the planning of paint preparation and application.
Assay method
The point in time at which a paint or resin begins to thicken or form a gel state after mixing can be measured by laboratory testing or the use of specific equipment.
Curing time
definition
Curing time refers to the time it takes for a coating to undergo further chemical cross-linking or other reactions after drying to form a final hardened or cured state. This process is a critical step in enabling the paint to achieve its final physical and chemical properties.
importance
The curing time affects the final properties of the coating, such as hardness, abrasion resistance, chemical resistance, and weather resistance. It usually takes a long time to complete, especially for coatings that require chemical cross-linking.
Assay method
Curing times are often determined by laboratory testing or by observing them for long periods of time in real-world applications. The degree of completion of curing can be judged by measuring changes in coating hardness, consumption of chemical reactions, or changes in other physical properties.
summary
Drying time is the time it takes for the paint to form a dry solid surface after application, mainly caused by the volatilization of solvents or moisture. Gelling timeIt is the time when the paint or resin begins to form a gelatinous or gel state after mixing.Curing timeIt is the time it takes for a coating to undergo chemical cross-linking or other reactions after drying to form a final hardened or cured state.
These time parameters are critical in the coatings and coating industry, and each reflects the physical and chemical changes at different stages of the coating curing process.






