Painting mass evaluation - Determination of coating Film thickness
Painted products have direct requirements for the thickness of the coating film according to their use and environmental conditions. In addition, the properties of the coating film also need to be based on the thickness as a conditional parameter, that is, the performance of the paint film is only comparable under the same thickness. Therefore, the thickness of the paint film is a very important control index in the process of coating construction.
The wet film thickness is used for the direct control and adjustment of the paint film thickness on the construction site, and the dry film thickness is used for quality monitoring and acceptance.
1. Wet film thickness determination
The thickness of the wet film is pressed vertically on the surface of the wet film with a serrated metal plate (wet film gauge - north and south tide injection) or disc (wet film wheel - north and south tide injection) with a sequential change of depth, and the serrated scale with the wet film is directly read.
2. Determination of dry film thickness
Dry film thickness determination is divided into two categories: magnetic method and eddy current method
(1) Magnetic method
The magnetic method is based on the magnetic flux or mutual inductance current of the probe on the magnetic substrate, and the linear change value of the magnetic flux or mutual inductance current of the mining head is used to determine the thickness of the coating by using the thickness of the non-magnetic coating on its surface. Therefore, the magnetic method is only suitable for measuring non-magnetic coatings on the surface of magnetic substrates.
According to its measuring principle. The test instrument is divided into two types: permanent magnet Thickness Gauge and electromagnetic induction Thickness Gauge. Permanent magnet Thickness Gauges have the advantages of simple structure, practicality, and low price, which are very suitable for carrying and field testing. The new permanent magnet gauge uses rare earth cobalt metal long-term magnets to make tungsten magnets that are wear-resistant and durable, but also maintain long-term accuracy. In addition, there is a pencil Thickness Gauge, which is not limited by surface shape and can measure on surfaces up to 230°C, with a measurement range of 5~500μm
Electromagnetic induction Thickness Gauge has been developed from the original pointer type to the digital display type, such as the coating Thickness Gauge of Defelsko in the United States.
When measuring the surface coating film of tinplate by magnetic method, because the tinplate is too thin (0.5-0.8mm), the measurement error is large, and the back of the tinplate can be lined with a thick iron plate or a standard substrate carried by the instrument for zeroing, standard and test measurement, and the average value of the upper, middle and lower three points is taken from the edge of the high test plate 1cm away. Some more professional Thickness Gauges (such as Defelsko advanced models) have the functions of automatic adjustment, data storage, statistics and printout, which can meet the requirements of IS09000 quality management standards.
(2) Eddy current method
The eddy current test probe has a built-in high-frequency current coil, which generates a high-frequency magnetic field in the tested coating, which causes eddy currents inside the metal matrix, and the magnetic field generated by the warm eddy current reacts on the coil in the probe, causing its impedance to change. With the change of the thickness of the surface coating, the distance between the probe and the metal changes, and the resistance of the reaction to the probe coil also changes accordingly, and the impedance of the probe coil is measured to reflect the thickness of the coating, and the eddy current method is suitable for measuring the thickness of the non-conductive coating on the non-magnetic metal matrix, and the thickness measurement of the non-magnetic coating on the surface of the magnetic substrate is also tried. And this type of Thickness Gauge usually has both electromagnetic and eddy current functions
(3) Other methods - ultrasonic method
Since the magnetic method and eddy current method can only measure the coating thickness on the surface of the metal matrix, for non-metallic matrix materials (such as material, wood, broken glass, etc.), it is necessary to use other methods such as the Positector 200 series of DeFelsko in the United States to use the ultrasonic principle and professional numerical control technology to carry out non-destructive thickness measurement of the surface coating of the non-metallic matrix.
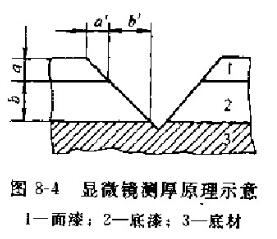 The above measurement methods are non-destructive thickness measurement, but as an arbitration method, the microscope method is still used, and the measurement principle is shown in Figure 8-4. The coating is notched in a "V" shape with an angled cutting tool up to the substrate, and the width of a' and b' is determined with a microscope with a ruler, the scale indexing has been converted to the micron scale by calibration coefficients, and the actual thickness of the paint mold (a and b) is read from the microscope.
The above measurement methods are non-destructive thickness measurement, but as an arbitration method, the microscope method is still used, and the measurement principle is shown in Figure 8-4. The coating is notched in a "V" shape with an angled cutting tool up to the substrate, and the width of a' and b' is determined with a microscope with a ruler, the scale indexing has been converted to the micron scale by calibration coefficients, and the actual thickness of the paint mold (a and b) is read from the microscope.
- 1Nondestructive measurement of dry coating thickness
- 2Determination method of dry and wet paint film thickness
- 3Coated steel coatings - Determination of dry-film thickness
- 4Wet film thickness measurement tool and applicable method
- 5Wet film thickness measurement and coating mass control
- 6Dry-film thickness measurement: an important step before Coating mass evaluation
- 7Application scheme of coating thickness test on wood board [with test video]
- 8Curved plastic coating thickness test application scheme [with test video]
- 9PosiTector200C ultrasonic coating Thickness Gauge on concrete coating thickness measurement application
-
-
-
-
-
JINGKELIAN QUL WFT gauge 0~500μm$ 123.00
-