How does a digital roughness meter measure concrete surface profile (CSP)?
Proper bonding of coatings and linings to concrete surfaces requires proper cleaning and often roughening of the concrete to increase the surface area. Roughness, also known as surface profile, can be imparted to concrete by blast cleaning, acid etching, or various impact/scratch power tools. The resulting depth of surface profile affects coating/lining adhesion and performance. Coating/lining manufacturers and/or facility owners often specify that concrete surfaces be cleaned and roughened prior to product installation.
Concrete Surface Profile (CSP) chips have traditionally been used to visually assess the surface profile (roughness) of prepared concrete, such as Guide No. 310.2R, Selection and Specification of Sealers, Coatings, Polymer Covers, and Concrete Surface Preparation of Concrete by Repairs produced by the International Concrete Repair Institute (ICRI). This guide summarizes the capabilities and limitations of the various methods used to prepare concrete surfaces for coating and repair. Chips are arguably the most widely recognized and commonly used method for assessing concrete roughness. However, this approach is qualitative and requires some judgment by the individual inspector.
More recently, digital options such as the PosiTector SPG TS allow inspectors to measure concrete surface profiles using digital qualitative methods according to ASTM D8271. While this method has significant benefits, its adoption has previously been limited by the CSP chip method (which reports the chip number closer to the concrete surface finish) and the digital depth micrometer method (where it is reported in mils).
However, in a recent paper by Beamish and Corbett (2022)1 a study was conducted to create a cross-reference table so that the two methods could be used interchangeably. See Appendix A of this article for details on the procedure used to create this table.
Evaluating Concrete Surface Profiles Using CSP Comparator Chips
ICRI Chips are available as a set of 10 with varying degrees of surface roughness indicating different methods of concrete surface preparation such as acid etching, grinding, shot peening, grit blasting and scratching. These chips are designed as visual and tactile comparators to identify surface roughness. The user compares the prepared concrete to the CSP chip and reports the chip number that is closer to the surface. Many jobs will specify the type of finish required.
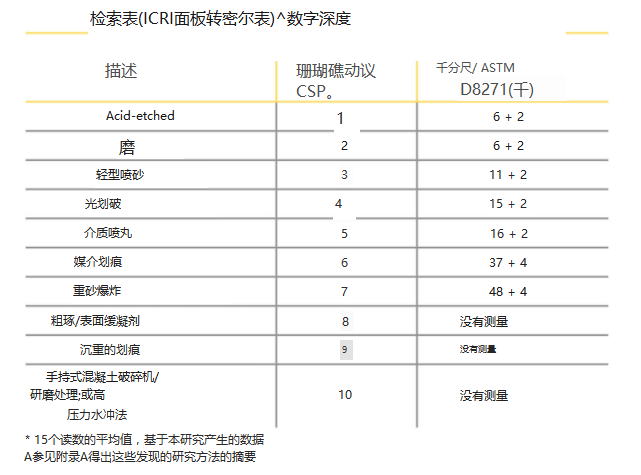
The ICRI CSP chip is approximately 16 inches square (3.5 inches x 4.5 inches) and is designed to replicate 10 surface profiles, as shown in Table 1.


Alternative Digital Measurement Solutions for Concrete Surface Profiles
ASTM D8271, Standard Test Method for Direct Measurement of Surface Profile of Precast Concrete, describes an alternative procedure for obtaining measurements directly from precast concrete using an electronic depth micrometer such as the PosiTector SPG TS. These instruments have a flat base and a spring-loaded tip that falls into the valleys of the surface contour.
The flat base of the PosiTector SPG TS gauge rests on the highest peak and each measurement is the distance between the highest local peak and a specific valley into which the tip projects. This type of instrument is ideal for measuring profile heights of up to 6 mm directly on surfaces without the need to replicate putty or the blurring of visual comparators. They are ideal for measuring the profile of concrete surfaces prepared by sandblasting, scratching, grinding, acid etching and other preparation methods.

Correlating direct measurements with visual assessment of concrete surface profile
Unlike qualitative visual comparators, ASTM D8271 is quantitative but has not been broadly specified. A study was performed using seven of ten ICRI CSP chips (CSP 1-7) of the PosiTector SPG TS digital depth micrometer (CSP 1-7) and the ASTM D8271 method using rigid epoxy cast replicas.
The lookup table shown below enables a specifier to easily convert a qualitative assessment (eg, ICRI CSP 1-7) into a quantitative range of concrete surface profiles. Only the range of CSP 1-7 is shown because these were the only ranges studied during this study and values have been rounded. Establish tolerances based on standard deviation data.
Advantages of Quantitative Measurements Using the PosiTector SPG TS Concrete Surface Profiler
Unlike subjective visual assessments, the digital PosiTector SPG TS Concrete Surface Profiler offers true quantitative analysis in the field of roughness measurement. The easy-to-use PosiTector SPG offers fast measurement speeds of over 50 readings per minute and onboard memory for record keeping, viewing and sharing with other users for further analysis.
Featuring a powerful statistical mode that displays mean, standard deviation, and min/max profile depth; the American-made PosiTector SPG is ideal for quickly and accurately analyzing large surfaces. The HiLo Alarm provides audible and visual alerts when measurements exceed user-specified limits. The PosiTector SPG features durable alumina wear faces and tungsten carbide probe tips designed for long life and continued accuracy.
确定是否符合混凝土表面轮廓规范
为了确定是否符合混凝土表面轮廓规范,AMPP 标准实践 SP21513,确定符合混凝土表面轮廓要求的程序概述了在何处进行测量以及进行多少次测量,并就如何识别不合格区域提供了指导。 本标准描述了适用于实验室和现场使用的程序,用于使用方法 1:ASTM D8271 中描述的深度千分尺和方法 2:混凝土表面轮廓 (CSP) 芯片 (CSP 1-10) 确定混凝土基材上指定表面轮廓的一致性 ICRI 指南 No. 310.2R 中描述。
附录 A:实验设计总结
研究设计最初由专门选择的方法组成,以使指定者能够从定性表面轮廓评估技术转换为定量范围。
使用数字深度千分尺 (ASTM D8271) 从 ICRI 混凝土表面轮廓 (CSP) 1-7 测量表面轮廓
ICRI CSP 芯片由灰色、柔韧的橡胶材料制成,这种材料对于大多数应用来说都是可接受的,但在这项研究中存在问题。用于测量这些 CSP 芯片表面轮廓的数字深度千分尺的探头包含一个不锈钢、弹簧加载的 60° 锥形点,该点会穿透柔韧的橡胶并产生虚假的高值。因此,制作了 CSP 1-7 的硅胶模具,并将黑色环氧树脂浇注到每个模具中,从而有效地在硬化环氧树脂中创建 CSP 1-7 的精确复制品,不受测微探头和压力的影响。
环氧树脂完全固化后,6 名技术人员(独立)使用量程高达 250 的 PosiTector SPG TS 数字深度千分尺(量具;图 6)在 CSP 1-7 复制品上获得三个子批次,每个批次 15 个读数mils 并存储在量具内存中以供后续分析。
在每种情况下,环氧树脂腻子复制品(间接测量方法)比直接测量方法(即直接从 CSP 芯片测量)产生更大的表面轮廓高度,并且数据的标准偏差更大。
结论
Proper bonding of coatings and linings to concrete surfaces requires proper cleaning and often roughening of the concrete to increase the surface area. Roughness, also known as surface profile, can be imparted to concrete by blast cleaning, acid etching, or various impact/scratch power tools. The resulting depth of surface profile affects coating/lining adhesion and performance. Coating/lining manufacturers and/or facility owners often specify that concrete surfaces be cleaned and roughened prior to product installation.
The CSP chip produced by ICRI is arguably the most widely recognized and commonly used method for assessing concrete roughness; however, this is qualitative and requires some judgment. The procedure described in ASTM D8271 is quantitative but not broadly specified at the time of writing.
This study demonstrates the discrepancy between direct measurements taken from known surfaces (ie, ICRI CSP panels) and indirect measurements obtained from epoxy putty castings of these same known surfaces. Therefore, when calling quantitative methods in contract documents (ASTM D8271), it is important for the specifier to indicate which method to use.
Lookup tables enable specifiers to easily translate qualitative methods into quantitative ranges for concrete surface profiles. Only the range of CSP 1-7 is shown as only these ranges were studied during this study. Values are rounded. Also, since measurements directly from the concrete are feasible, there is little value in using epoxy putty to generate a replica of the concrete surface (and subsequently measuring with a micrometer) unless the concrete roughness needs to be documented.
- 1Film adhesion detection method and its applicability analysis
- 2Purpose, method, principle and operation points of coating adhesion test
- 3Working principle and application of UV coating Cupping testing device
- 4Principle and Application Analysis of Film Adhesion Tester
- 5Optical inspection device Anti-reflection film adhesion Measuring method
- 6Automatic scratch test to evaluate film strength, hardness, adhesion
- 7Comparison of film adhesion determination methods
- 8Determination of film adhesion
- 9Paint film adhesion and test method thereof
-
-
KAIRDA NDT151P Roughness Gauge$ 810.00
-
-
-
-






