What causes adhesion test failure?
What does a failed adhesion test mean?
Adhesion test failure is the failure of a coating to adhere to a substrate when tested for adhesion according to the ASTM D 4541 standard specification.
Adhesive strength and performance of industrial paints and coatings are tested with the help of a pull-out apparatus consisting of a short drawn tube bonded to the surface of the coating. Once the coating is dry and the bond is firm, the pulling force is applied by the puller and increased until the coating separates. This force is recorded by the slider and checked to see if it is within the allowable range for the bond strength. If the coating peels off before the allowable force limit, it is said to have failed the adhesion test.
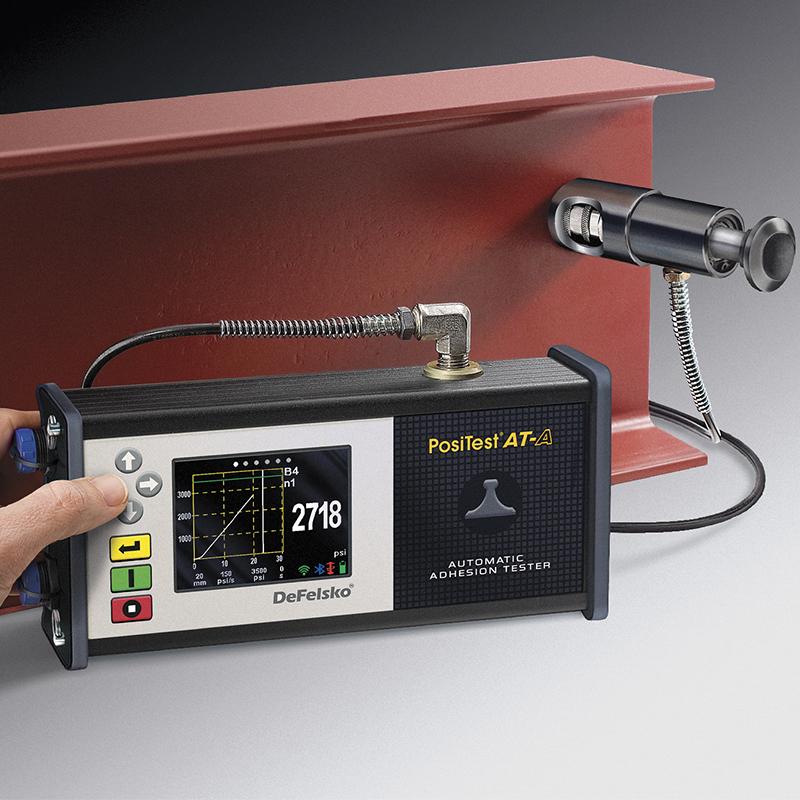

Strong adhesion of a coating or paint depends on various factors such as:
Physical properties of substrate and coating
Surface geometry to which the coating has been applied
Test Parameters, Conditions and Types of Instruments Used to Check Bond Strength
Test Methods
operator skills
Consistency and rate of applied tension or load
If any factor is insufficient, the chances of failing the adhesion test increase. To test for bond strength, a perpendicular tensile load is applied and the amount of tensile force or load is recorded at which the coating breaks from the substrate (i.e., when the coating separates). The test is performed by fixing a loading jig (cart) perpendicular to the coated surface with an adhesive. Gradually increase the tension and check the deformation of the coated surface. Increasing the force until complete deformation of the coating occurs breaks the bond between the coating and the substrate.
-
KOSON KS-10C coating Adhesion Tester$ 540.00
-
-
- 1Film adhesion detection method and its applicability analysis
- 2Purpose, method, principle and operation points of coating adhesion test
- 3Working principle and application of UV coating Cupping testing device
- 4Principle and Application Analysis of Film Adhesion Tester
- 5Optical inspection device Anti-reflection film adhesion Measuring method
- 6Automatic scratch test to evaluate film strength, hardness, adhesion
- 7Comparison of film adhesion determination methods
- 8Determination of film adhesion
- 9Paint film adhesion and test method thereof
-
-
-
-
-
RUNJIE RJ-M Adhesion Tester 14mm$ 1227.00
-