
Qiwei DDS-307 microcomputer conductivity meter 0~1999μs/cm
SE-
 AOLILONG DDS-307 Digital Display Conductivity Meter Conductivity Detector$ 127.00SE
AOLILONG DDS-307 Digital Display Conductivity Meter Conductivity Detector$ 127.00SE -
 YueFeng DDS-307 LABOratory conductivity meter 0.00μS/cm~ 100mS/cm$ 209.00SE
YueFeng DDS-307 LABOratory conductivity meter 0.00μS/cm~ 100mS/cm$ 209.00SE -
 YueFeng DDS-307A LABOratory conductivity meter 0.00μS/cm~ 100mS/cm$ 226.00SE
YueFeng DDS-307A LABOratory conductivity meter 0.00μS/cm~ 100mS/cm$ 226.00SE -
 LEICI DDS-307A Conductivity Meter conductivity TDS Temperature Class 1.0$ 494.00SE
LEICI DDS-307A Conductivity Meter conductivity TDS Temperature Class 1.0$ 494.00SE -
 LEICI DDS-307 Conductivity Meter Class 1.0$ 411.00SE
LEICI DDS-307 Conductivity Meter Class 1.0$ 411.00SE
QiWei DDS-307 Conductivity Meter (microcomputer type)SPEC
QiWei DDS-307 Conductivity Meter (microcomputer type)Details
QiWei DDS-307 Conductivity Meter (microcomputer type)Packing list
- SKU
- NB000994
- Measurement parameters
- Conductivity Detector
- Measuring range
- 0~199.9μs/cm;200~1999μs/cm;2.00~19.99mS/cm;20.0~199.9mS/cm
- Measurement error
- ±1.0% F.S
- resolution
- 0.1/1μs/cm;0.01/0.1ms/cm
- Temperature compensation range
- 0~50℃
- data storage
- 50 groups
- Power
- DC9V Adapter
- Dimensions
- 220*200*80mm
- Weight
- 1.7KG
- Electrode constant specification
- 0.1、1、10
- temperature coefficient
- 2%/℃
- Save content
- Numbers, measurements, Measurement Units and temperature values
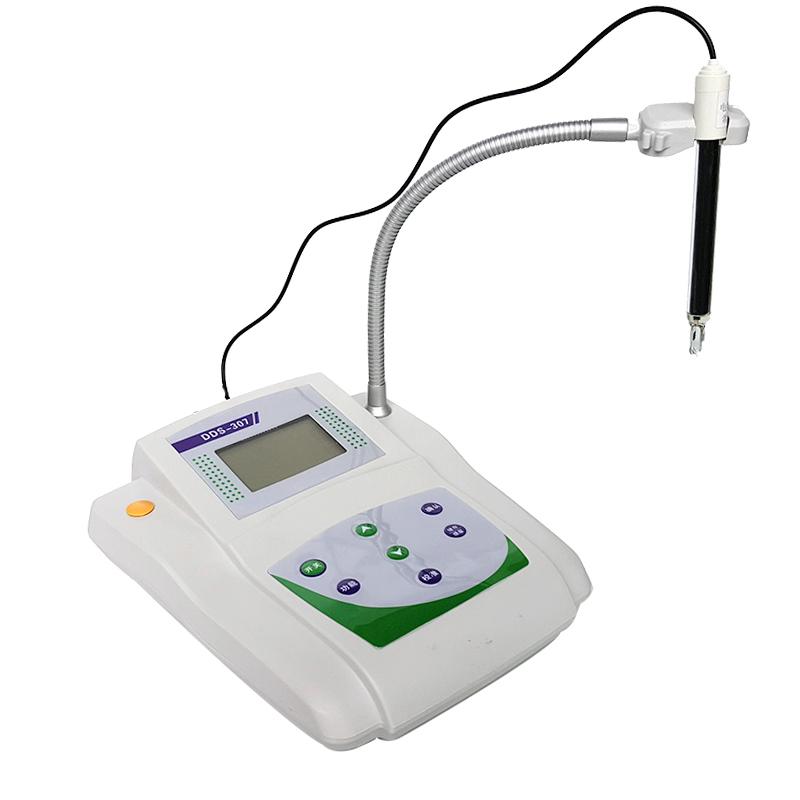
Introduction
Qiwei DDS-307 conductivity meter is a microcomputer-based precision conductivity meter, equipped with a temperature electrode, which can automatically compensate the temperature and maintain a more balanced experimental environment temperature. The measurement range of DDS-307 conductivity meter is (0~199.9) μs/cm; (200~1999) μs/cm; (2.00~19.99) ms/cm; (20.0~199.9) ms/cm, which can store serial number, Measured value, unit of measure and temperature value, convenient for follow-up data tracking. The measurement is stable and convenient.
Product principle
In an electrolyte solution, charged ions move under the action of an electric field to transmit electric current. Its conductivity is represented by the conductivity G, which is the reciprocal of the resistance. That is, G=1/R
The method of testing the conductivity is to insert an electrode composed of two metal plates into the solution to form a conductivity cell, and measure the resistance between the two plates. According to Ohm's law, the resistance value is proportional to the distance L (cm) between the plates and inversely proportional to the area A (cm2) of the plates. That is, R=ρ•L/A
ρ is the resistivity, let its reciprocal be the conductivity and expressed in K, then K=1/ρ
For a certain electrode, the ratio of the effective distance L between the electrode plates to the area A of the plates is called the electrode constant of this electrode, expressed in J, that is, J=L/A
According to the above formulas, it can be obtained: G=K/J, that is, K=G·J
The unit of conductance G is Siemens, and the unit symbol is S.
1S=103ms=106μS
The commonly used units of conductivity K are mS/cm and μS/cm.
Test Principle
The method of DDS-307 conductivity meter to test the conductance is to apply the AC Voltage generated by the oscillator to the electrode (the purpose of applying the AC Voltage is to avoid the polarization of the electrode), and a current is generated in the conductivity cell, which is consistent with the measured current. The conductivity of the solution is proportional to the current-Voltage conversion, amplification, detection, conversion to DC Voltage, temperature compensation, etc., and finally converted into a digital signal by the A/D converter, which is displayed by a microcomputer. The whole process is controlled and processed by microcomputer.
Pictures

- 1JJG 2059-2014《Measuring Instruments for Electrolytic Conductivity》
- 2JB/T 9366-2017《Laboratory conductivity meters》
- 3SL 78-1994《Determination of conductivity (Conductivity instrument method)》
- 4GB/T 12582-1990《Liquid hydrocarbons--Determination of electrical conductivity--PrecisIon Meter》
- 5GB/T 13580.3-1992《Determination of specific conductance in the wet precipitation》
- 6GB/T 6539-1997《Standard test methods for electrical conductivity of aviation and distillate fuels》
- 7GB/T 18932.15-2003《Method for the determination of electrical conduct-ivity in honey》
- 8GB/T 11007-2008《Test method of electrolytic conductivity analyzers》
- 9GB/T 23977-2009《Dyestuffs - Determination of content of salt - Conductance method》
- 10GB/T 41079.2-2022《Test methods for physical properties of liquid metals—Part 2: Determination of electrical conductivity》
 DDS-307
DDS-307





