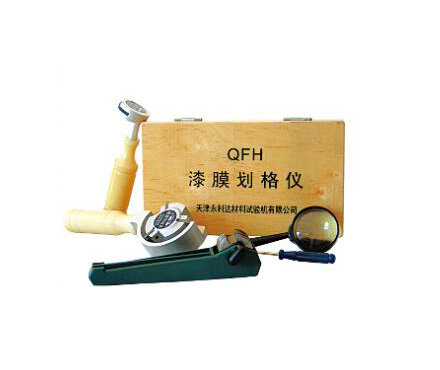
The principle, application, test procedure and result evaluation of cross-cut Tester
Overview
The cross-cut Tester is a commonly used tool for evaluating the adhesion and durability of coatings, such as paints, varnishes, and other protective coatings, on different substrates. It is a qualitative test that assesses the resistance of a coating to cracking, flaking, or detachment from the substrate.
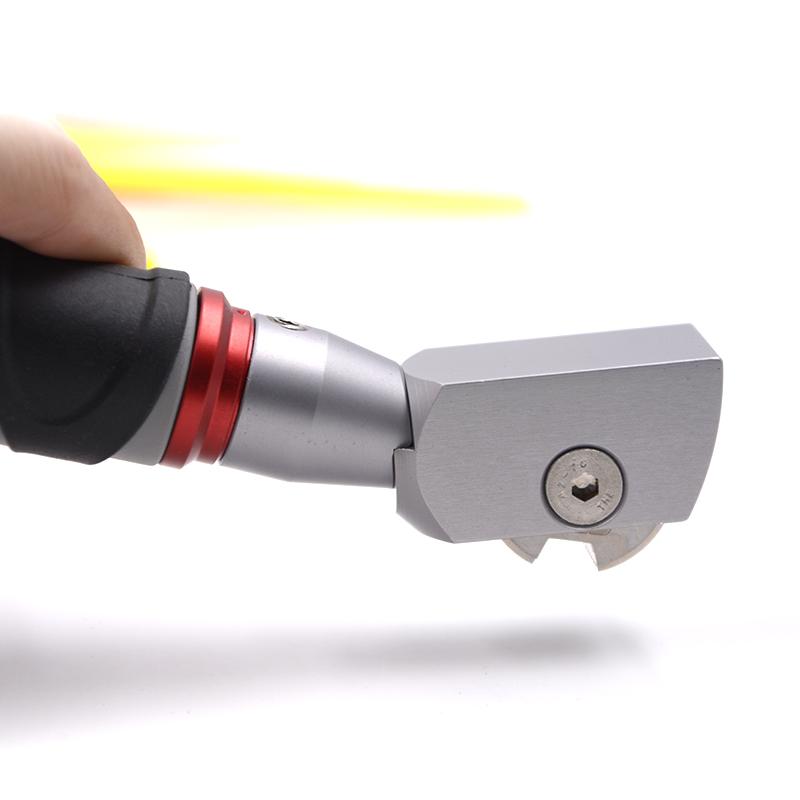

Principle
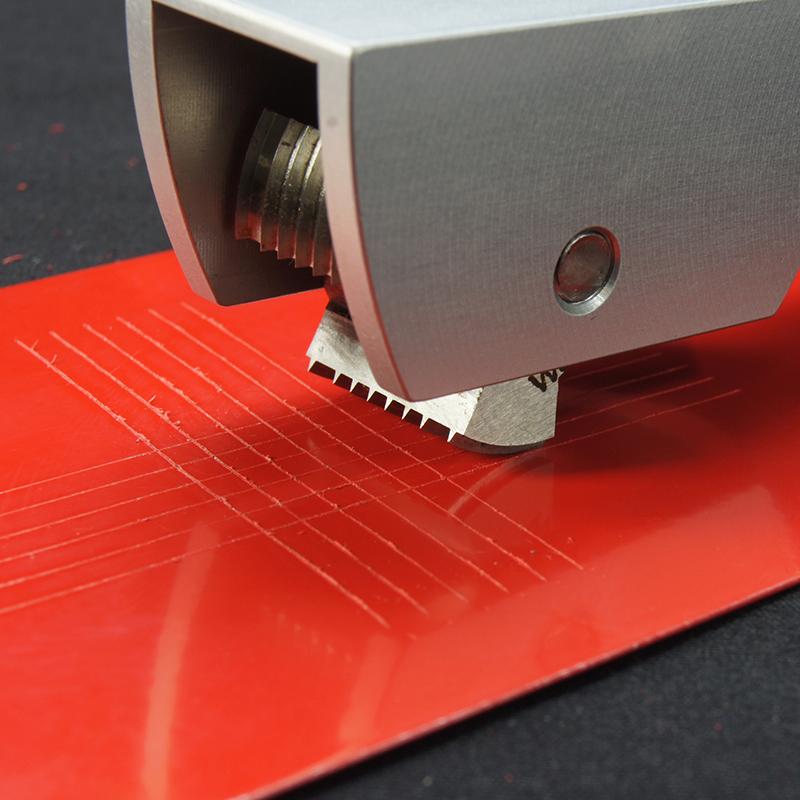
The principle of the cross-cut test involves making a series of perpendicular cuts or incisions through the coating using a sharp blade, usually in the form of a grid or a lattice pattern. The cuts are made to reach the substrate, and the resulting pattern resembles a cross or grid, hence the name "cross-cut Tester." After making the cuts, the surface is typically cleaned to remove any loose debris, and the adhesion of the coating is visually evaluated. The test is usually performed according to a specific standard, such as ASTM D3359 or ISO 2409, which provides guidelines for the size, spacing, and number of cuts to be made, as well as the criteria for evaluating the adhesion of the coating.
Application
The cross-cut Tester is widely used in various industries, such as automotive, aerospace, marine, construction, and coatings manufacturing, to assess the quality and durability of coatings. It is a simple and relatively inexpensive test that provides qualitative information about the adhesion performance of a coating under standard conditions. However, it should be noted that the cross-cut test is a destructive test and may not provide quantitative data on the exact adhesion strength or performance of a coating. For more precise adhesion testing, other methods, such as pull-off adhesion testing or instrumented scratch testing, may be used in conjunction with the cross-cut test.
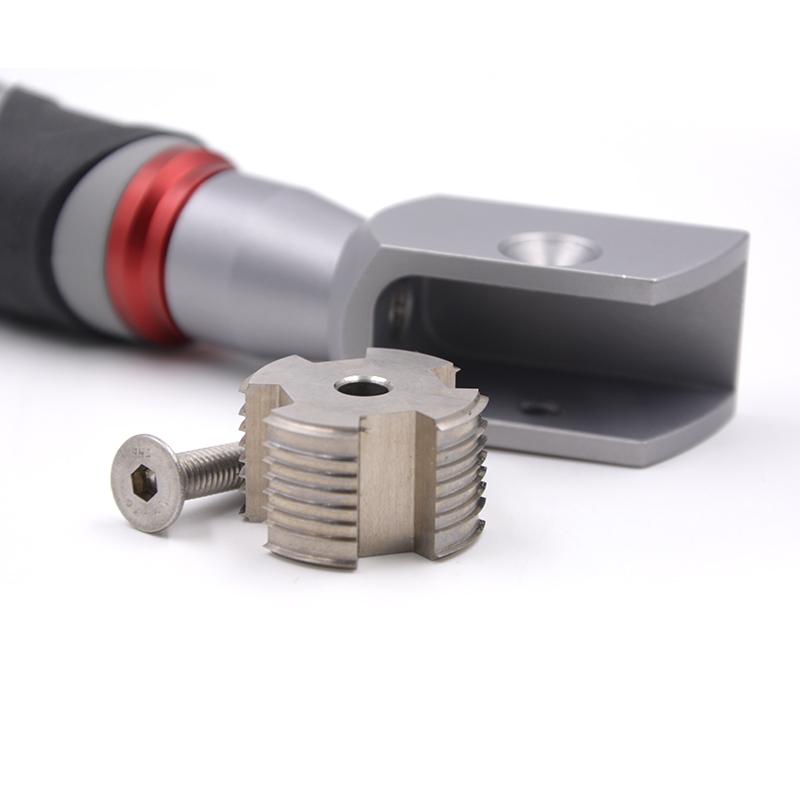

Test steps
The cross-cut test typically involves making a series of parallel cuts using a cutting tool, such as a sharp blade or a specialized cutting tool, on the coated surface. The cuts are usually spaced at a specific distance, such as 1 mm or 2 mm, and are then repeated at right angles to create a grid or lattice pattern. The number of cuts made depends on the standard or specification being followed, but typically ranges from 5 to 11 cuts in each direction, resulting in a total of 25 to 121 squares or rectangles. After making the cuts, the surface is often cleaned to remove any loose debris, and the adhesion of the coating is visually evaluated or assessed using a standard rating scale.
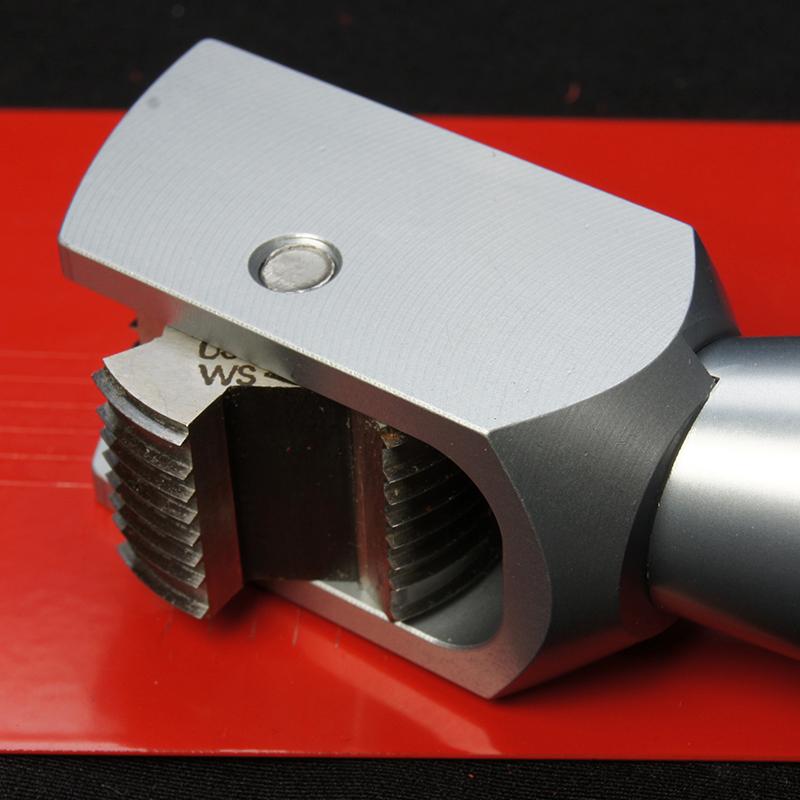

How to evaluate
The adhesion of the coating is typically evaluated based on the extent and type of coating detachment or loss observed after the cross-cut test. Common evaluation criteria include the percentage of coating loss, the size of the detached or flaked areas, and the type of coating failure, such as cohesive failure (within the coating) or adhesive failure (between the coating and substrate). The evaluation is usually performed based on a standard rating scale, which may range from 0 (no coating loss) to 5 (severe coating loss), with intermediate ratings indicating varying degrees of adhesion performance.
Interpretation of Results
The results of the cross-cut test can provide an indication of the adhesion performance and durability of the coating. If the coating shows minimal or no coating loss after the test, it is generally considered to have good adhesion. However, if significant coating loss or detachment is observed, it may indicate poor adhesion, which may lead to potential issues such as corrosion, peeling, or flaking of the coating in real-world service conditions.
Conclusion
The cross-cut test has some limitations. It is a qualitative test and may not provide precise quantitative data on the adhesion strength of the coating. The test conditions, such as the size and spacing of the cuts, the cutting tool used, and the evaluation criteria, may vary depending on the standard or specification being followed, which can affect the test results. Additionally, the cross-cut test may not fully represent the actual performance of the coating in real-world service conditions, as it is a controlled laboratory test and does not consider factors such as exposure to environmental conditions, cyclic loading, or other specific service conditions.
Anyway, the cross-cut test is a widely used method for assessing the adhesion and durability of coatings on various substrates. It is a simple and relatively inexpensive test that provides qualitative information about the adhesion performance of a coating under standard conditions. However, it should be used in conjunction with other testing methods and should be interpreted cautiously, taking into consideration the specific test conditions and limitations associated with the test.
- 1Film adhesion detection method and its applicability analysis
- 2Purpose, method, principle and operation points of coating adhesion test
- 3Working principle and application of UV coating Cupping testing device
- 4Principle and Application Analysis of Film Adhesion Tester
- 5Optical inspection device Anti-reflection film adhesion Measuring method
- 6Automatic scratch test to evaluate film strength, hardness, adhesion
- 7Comparison of film adhesion determination methods
- 8Determination of film adhesion
- 9Paint film adhesion and test method thereof