Coating performance testing: the key to ensuring quality coatings
Coatings play an important role in industry and construction to protect, beautify and enhance the performance of materials. To ensure coating mass, a series of performance tests must be performed to achieve excellent results in practical applications. This article will delve into all aspects of coating performance testing, including adhesion, flexibility, Impact strength, hardness, Gloss, heat resistance, ageing resistance, abrasion resistance, and Miscellaneous performance indicators.
1. Adhesion
Adhesion refers to the degree of strong bonding between the coating and the surface of the coating. This bonding force depends on the interaction between the polymer groups in the coating (such as hydroxyl or carboxyl groups) and the polar groups on the surface of the coating. The quality of adhesion can be affected by a number of factors, including contamination, moisture, cissing stress of the coating, and degree of crosslinking. Coating adhesion is measured by cross-cut, circle-drawing, tensile, and solvent testing. These methods help ensure that the coating adheres tightly to the surface of the coating without peeling or disbonding.
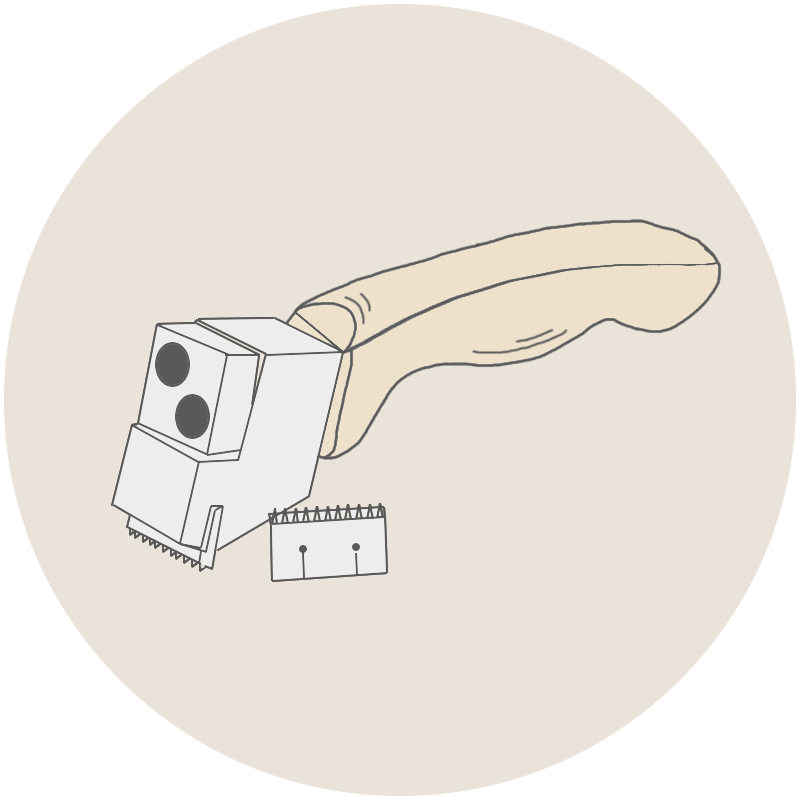
2. Flexibility
Flexibility refers to the performance of a coating that remains intact without cracking or disbonding when subjected to bending or deformation. Coating flexibility is often affected by the flexibility of the film formation material and the crosslinking Density. Determination of coating flexibility involves bending painted samples on shafts of different diameters using a shafts Tester to determine the minimum diameter, which is an indicator of coating flexibility.
3. Impact strength
Impact strength assesses the resistance of coatings to impact at high velocities, especially for metallic materials. Coatings with good impact strength are not prone to cracking or disbonding under impact conditions. Impact strength is measured by using an impact Tester to assess the performance of the coating by dropping a weight of a certain mass. Impact strength is usually expressed in "kg · cm".

4. Hardness
Hardness is the resistance of the coating surface to objects and is one of the mechanical strengths of coatings. The hardness of coatings is usually affected by the characteristics of the film formation material and the degree of cross-linking. Different hardness measurement methods include Pendulum damping hardness method, pencil hardness method, scratch hardness method and indentation hardness method. These methods can be used to measure the hardness of coatings, helping to assess their mass and durability.
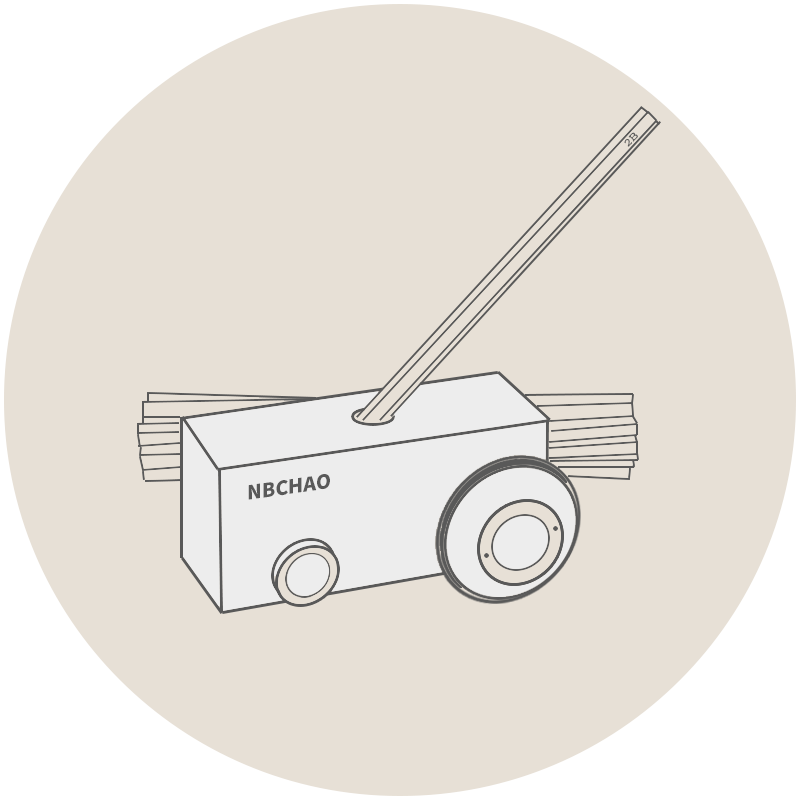
5. Gloss
Gloss is a property of the reflection ability of a coating surface under rays of light. Gloss is usually expressed numerically, reflecting the specular degree of the coating surface. Gloss determination is usually performed using a Glossmeter, which is one of the key indicators for evaluating the coating Appearance mass.
6. Heat resistance and ageing resistance
Heat resistance assesses the ability of a coating to maintain its performance at elevated temperatures. Ageing resistance assesses the performance of coatings under the influence of environmental factors such as light, heat and oxidation. These performance indicators are critical for coatings in specific application environments and are therefore often regarded as important indicators of coating mass.
7. Abrasion resistance
Abrasion resistance refers to the resistance of coatings to friction and abrasion. Commonly used abrasion resistance measurement methods include using a coating abrasion resistor to test coatings under a certain load. Smaller weight loss values indicate better abrasion resistance, which is important for applications that require frequent abrasion such as road sign paints and floor paints.
8. Miscellaneous performance
In addition to the above performance indicators, there are some Miscellaneous performance parameters to consider. Light retention assesses the ability of coatings to maintain Gloss under light conditions, while water resistance tests the resistance of coatings to water. Performance parameters such as solvent resistance and temperature resistance can also be critical for coatings for specific applications.
In coating performance testing, appropriate test methods and standards are the key to ensuring coating mass. By considering these performance parameters comprehensively, coating manufacturers and users can choose the coating that best suits their needs and ensure its excellent performance and Reliability in practical applications. Through rigorous performance testing, coatings can be ensured to perform well in various environment conditions, providing long-lasting protection and aesthetic results.
- 1Film adhesion detection method and its applicability analysis
- 2Purpose, method, principle and operation points of coating adhesion test
- 3Working principle and application of UV coating Cupping testing device
- 4Principle and Application Analysis of Film Adhesion Tester
- 5Application of shakeout Tester in organic polymer film abrasion resistance testing
- 6Application of shakeout Tester in aluminum surface coating abrasion resistance testing
- 7Optical inspection device Anti-reflection film adhesion Measuring method
- 8Automatic scratch test to evaluate film strength, hardness, adhesion
- 9Comparison of film adhesion determination methods




